p27 Is a Candidate Prognostic Biomarker and Metastatic Promoter in Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 27197201
- PMCID: PMC4930684
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3189
p27 Is a Candidate Prognostic Biomarker and Metastatic Promoter in Osteosarcoma
Abstract
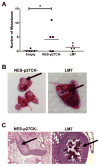
Metastatic progression is the major cause of death in osteosarcoma, the most common bone malignancy in children and young adults. However, prognostic biomarkers and efficacious targeted treatments for metastatic disease remain lacking. Using an immunoproteomic approach, we discovered that autoantibodies against the cell-cycle kinase inhibitor p27 (KIP1, CDKN1B) were elevated in plasma of high-risk osteosarcoma patients. Using a large cohort of serum samples from osteosarcoma patients (n = 233), we validated that a higher level of the p27 autoantibody significantly correlated with poor overall and event-free survival (P < 0.05). Immunohistochemical analysis also showed that p27 was mislocalized to the cytoplasm in the majority of osteosarcoma cases and in highly metastatic osteosarcoma cell lines. We demonstrated that ectopic expression of cytoplasmic p27 promoted migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells, whereas shRNA-mediated gene silencing suppressed these effects. In addition, mutations at the p27 phosphorylation sites S10 or T198, but not T157, abolished the migratory and invasive phenotypes. Furthermore, the development of pulmonary metastases increased in mice injected with cells expressing cytoplasmic p27 compared with an empty vector control. Collectively, our findings support further investigation of p27 as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in osteosarcoma cases exhibiting aberrant p27 subcellular localization. Cancer Res; 76(13); 4002-11. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Chou AJ, Geller DS, Gorlick R. Therapy for osteosarcoma: where do we go from here? Paediatr Drugs. 2008;10(5):315–27. - PubMed
-
- Link MP, Eilber F. Osteosarcoma. In: Eilber F, Poplack D, editors. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology. 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1997. pp. 889–920.
-
- Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G, Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, et al. Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: an analysis of 1,702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(3):776–90. - PubMed
-
- Kager L, Zoubek A, Potschger U, Kastner U, Flege S, Kempf-Bielack B, et al. Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: presentation and outcome of patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(10):2011–18. - PubMed
-
- Bacci G, Briccoli A, Rocca M, Ferrari S, Donati D, Longhi A, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma of the extremities with metastases at presentation: recent experience at the Rizzoli Institute in 57 patients treated with cisplatin, doxorubicin, and a high dose of methotrexate and ifosfamide. Ann Oncol. 2003;14(7):1126–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

