Association Analysis of the Cubilin (CUBN) and Megalin (LRP2) Genes with ESRD in African Americans
- PMID: 27197912
- PMCID: PMC4891762
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12971215
Association Analysis of the Cubilin (CUBN) and Megalin (LRP2) Genes with ESRD in African Americans
Abstract
Background and objectives: Genetic variation in the cubilin (CUBN) gene is associated with albuminuria and CKD. Common and rare coding variants in CUBN and the gene encoding its transport partner megalin (LRP2) were assessed for association with ESRD in blacks.
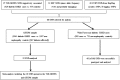
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Sixty-six CUBN and LRP2 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were selected and analyzed in this multistage study. Exome sequencing data from 529 blacks with type 2 diabetes (T2D) -associated ESRD and 535 controls lacking T2D or nephropathy (the Type 2 Diabetes Genes [T2D-GENES] Consortium) were first evaluated, focusing on coding variants in CUBN and LRP2; 15 potentially associated SNPs identified from the T2D-GENES Consortium as well as 51 other selected SNPs were then assessed in an independent T2D-ESRD sample set of blacks (the Affymetrix Axiom Biobank Genotyping Array [AXIOM]; 2041 patients with T2D-ESRD, 627 patients with T2D without nephropathy, and 1140 nondiabetic, non-nephropathy controls). A meta-analysis combining the T2D-GENES Consortium and the AXIOM data was performed for 18 overlapping SNPs. Additionally, all 66 SNPs were genotyped in the Wake Forest School of Medicine samples of blacks with nondiabetic ESRD (885 patients with nondiabetic ESRD and 721 controls). Association testing with ESRD was performed in models including age, sex, African ancestry proportion, and apolipoprotein L1 gene renal-risk variants.
Results: CUBN SNP rs1801239 (I2984V), previously associated with albuminuria, was significantly associated with T2D-ESRD in blacks (the T2D-GENES Consortium and the AXIOM meta-analysis, P=0.03; odds ratio, 1.31; 95% confidence interval, 1.03 to 1.67; minor allele frequency =0.028). A novel LRP2 missense variant, rs17848169 (N2632D), was also significantly protective from T2D-ESRD (the T2D-GENES Consortium and the AXIOM, P<0.002; odds ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.29 to 0.75; meta-analysis minor allele frequency =0.007). Neither SNP was associated with T2D when contrasting patients with T2D with controls lacking diabetes. CUBN and LRP2 SNPs were not associated with nondiabetic etiologies of ESRD.
Conclusions: Evidence for genetic association exists between a cubilin and a rare megalin variant with diabetes-associated ESRD in populations with recent African ancestry.
Keywords: African Americans; Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2; Genotype; Humans; Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide; Renal Insufficiency, Chronic; albuminuria; chronic kidney disease; diabetic nephropathy; end stage kidney disease.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Beyond APOL1: Genetic Inroads into Understanding Population Disparities in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jun 6;11(6):928-931. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04680416. Epub 2016 May 19. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27197913 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Köttgen A: Genome-wide association studies in nephrology research. Am J Kidney Dis 56: 743–758, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Freedman BI, Tuttle AB, Spray BJ: Familial predisposition to nephropathy in African-Americans with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Kidney Dis 25: 710–713, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Saran R, Li Y, Robinson B, Ayanian J, Balkrishnan R, Bragg-Gresham J, Chen JT, Cope E, Gipson D, He K, Herman W, Heung M, Hirth RA, Jacobsen SS, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP, Leichtman AB, Lu Y, Molnar MZ, Morgenstern H, Nallamothu B, O'Hare AM, Pisoni R, Plattner B, Port FK, Rao P, Rhee CM, Schaubel DE, Selewski DT, Shahinian V, Sim JJ, Song P, Streja E, Kurella Tamura M, Tentori F, Eggers PW, Agodoa LY, Abbott KC: US Renal Data System 2014 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 66[1 Suppl 1]: S1–S105, 2015 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kopp JB, Nelson GW, Sampath K, Johnson RC, Genovese G, An P, Friedman D, Briggs W, Dart R, Korbet S, Mokrzycki MH, Kimmel PL, Limou S, Ahuja TS, Berns JS, Fryc J, Simon EE, Smith MC, Trachtman H, Michel DM, Schelling JR, Vlahov D, Pollak M, Winkler CA: APOL1 genetic variants in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and HIV-associated nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 22: 2129–2137, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical