Policy to practice: impact of GeneXpert MTB/RIF implementation on the TB spectrum of care in Lilongwe, Malawi
- PMID: 27198215
- PMCID: PMC4914880
- DOI: 10.1093/trstmh/trw030
Policy to practice: impact of GeneXpert MTB/RIF implementation on the TB spectrum of care in Lilongwe, Malawi
Abstract
Background: While previous research has provided evidence of the diagnostic accuracy of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF (GeneXpert), further information is needed about implementation in the real-world. This study evaluated the impact of the introduction of GeneXpert testing in a tertiary medical center according to the testing algorithm proposed by the National TB Control Program (NTP) guidelines.
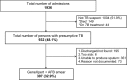
Methods: All adult medicine inpatient persons with presumptive TB admitted between November 2013 and March 2014 were eligible for GeneXpert sputum testing and followed to TB treatment initiation status.
Results: We identified 932 persons with presumptive TB, of which 307 (32.9%) were GeneXpert tested. Those tested had an average age of 40 years, 49.2% (151) were male, 34.5% (106) were HIV positive, and 84.1% (249) presented with a cough. Of those GeneXpert tested, 28/307 (9.1%) tested positive, a 55.5% increase in detection compared to smear microscopy. However, the majority (44/72, 61%) of TB diagnoses were made by other modalities and not confirmed microbiologically. Of the 58 patients recommended to start treatment and discharged from the hospital, only 23 (40%) were documented to have started treatment at regional directly observed treatment short (DOTS) centers.
Conclusions: GeneXpert contributed minimally to overall TB diagnosis and the cascade of care due to implementation challenges of sputum collection, empiric treatment, and weak linkage to care between inpatient and outpatient settings.
Keywords: Diagnosis; GeneXpert; GeneXpert negative TB; HIV; Malawi; Pulmonary tuberculosis.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- WHO WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2013. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Steingart KR, Ng V, Henry M et al. Sputum processing methods to improve the sensitivity of smear microscopy for tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 2006;6:664–74. - PubMed
-
- Corbett EL, Marston B, Churchyard GJ et al. Tuberculosis in sub-Saharan Africa: opportunities, challenges, and change in the era of antiretroviral treatment. Lancet 2006;367:926–37. - PubMed
-
- WHO; Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children. Policy update. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

