The RING 2.0 web server for high quality residue interaction networks
- PMID: 27198219
- PMCID: PMC4987896
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw315
The RING 2.0 web server for high quality residue interaction networks
Abstract
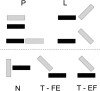
Residue interaction networks (RINs) are an alternative way of representing protein structures where nodes are residues and arcs physico-chemical interactions. RINs have been extensively and successfully used for analysing mutation effects, protein folding, domain-domain communication and catalytic activity. Here we present RING 2.0, a new version of the RING software for the identification of covalent and non-covalent bonds in protein structures, including π-π stacking and π-cation interactions. RING 2.0 is extremely fast and generates both intra and inter-chain interactions including solvent and ligand atoms. The generated networks are very accurate and reliable thanks to a complex empirical re-parameterization of distance thresholds performed on the entire Protein Data Bank. By default, RING output is generated with optimal parameters but the web server provides an exhaustive interface to customize the calculation. The network can be visualized directly in the browser or in Cytoscape. Alternatively, the RING-Viz script for Pymol allows visualizing the interactions at atomic level in the structure. The web server and RING-Viz, together with an extensive help and tutorial, are available from URL: http://protein.bio.unipd.it/ring.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Cockroft S.L., Hunter C.A. Chemical double-mutant cycles: dissecting non-covalent interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007;36:172–188. - PubMed
-
- Vishveshwara S., Ghosh A., Hansia P. Intra and inter-molecular communications through protein structure network. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009;10:146–160. - PubMed
-
- Csermely P. Creative elements: network-based predictions of active centres in proteins and cellular and social networks. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008;33:569–576. - PubMed
-
- Yan W., Sun M., Hu G., Zhou J., Zhang W., Chen J., Chen B., Shen B. Amino acid contact energy networks impact protein structure and evolution. J. Theor. Biol. 2014;355:95–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

