Skeletal muscle fiber analysis by atmospheric pressure scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging at high mass and high spatial resolution
- PMID: 27198224
- PMCID: PMC5555214
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201500536
Skeletal muscle fiber analysis by atmospheric pressure scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging at high mass and high spatial resolution
Abstract
Skeletal muscles are composed of heterogeneous muscle fibers with various fiber types. These fibers can be classified into different classes based on their different characteristics. MALDI mass spectrometric imaging (MSI) has been applied to study and visualize different metabolomics profiles of different fiber types. Here, skeletal muscles were analyzed by atmospheric pressure scanning microprobe MALDI-MSI at high spatial and high mass resolution.
Keywords: Atmospheric pressure MALDI mass spectrometric imaging; Biomedicine; High mass resolution MS; High spatial resolution MS; Metabolomics; Skeletal muscle fiber type.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
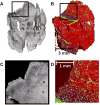
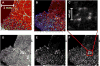
References
-
- Bouschen W, Schulz O, Eikel D, Spengler B, et al. Matrix vapor deposition/recrystallization and dedicated spray preparation for high-resolution scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization imaging mass spectrometry (SMALDI-MS) of tissue and single cells. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010;24:355–364. - PubMed
-
- Paschke C, Leisner A, Hester A, Maass K, et al. Mirion–a software package for automatic processing of mass spectrometric images. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013;24:1296–1306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

