Multifunctional hydrogel nano-probes for atomic force microscopy
- PMID: 27199165
- PMCID: PMC4876479
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11566
Multifunctional hydrogel nano-probes for atomic force microscopy
Abstract
Since the invention of the atomic force microscope (AFM) three decades ago, there have been numerous advances in its measurement capabilities. Curiously, throughout these developments, the fundamental nature of the force-sensing probe-the key actuating element-has remained largely unchanged. It is produced by long-established microfabrication etching strategies and typically composed of silicon-based materials. Here, we report a new class of photopolymerizable hydrogel nano-probes that are produced by bottom-up fabrication with compressible replica moulding. The hydrogel probes demonstrate excellent capabilities for AFM imaging and force measurement applications while enabling programmable, multifunctional capabilities based on compositionally adjustable mechanical properties and facile encapsulation of various nanomaterials. Taken together, the simple, fast and affordable manufacturing route and multifunctional capabilities of hydrogel AFM nano-probes highlight the potential of soft matter mechanical transducers in nanotechnology applications. The fabrication scheme can also be readily utilized to prepare hydrogel cantilevers, including in parallel arrays, for nanomechanical sensor devices.
Figures
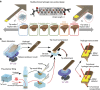


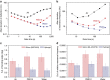
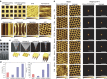
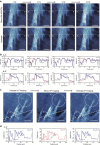

Similar articles
-
Focused ion beam-assisted fabrication of soft high-aspect ratio silicon nanowire atomic force microscopy probes.Ultramicroscopy. 2017 Aug;179:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2017.03.031. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Ultramicroscopy. 2017. PMID: 28384541
-
Novel ultrananocrystalline diamond probes for high-resolution low-wear nanolithographic techniques.Small. 2005 Aug;1(8-9):866-74. doi: 10.1002/smll.200500028. Small. 2005. PMID: 17193541
-
High-resolution noncontact atomic force microscopy.Nanotechnology. 2009 Jul 1;20(26):260201. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/26/260201. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Nanotechnology. 2009. PMID: 19531843
-
Nanoelectrodes integrated in atomic force microscopy cantilevers for imaging of in situ enzyme activity.Methods Mol Biol. 2005;300:403-15. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-858-7:403. Methods Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657494 Review.
-
Atomic force microscope as a nano- and micrometer scale biological manipulator: A short review.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Jan;73:132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.07.031. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 28739341 Review.
Cited by
-
3D-printed cellular tips for tuning fork atomic force microscopy in shear mode.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 12;11(1):5732. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19536-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33184281 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of sharp silicon nitride tips into high-speed SU8 cantilevers in a batch fabrication process.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2019 Nov 29;10:2357-2363. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.10.226. eCollection 2019. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31886112 Free PMC article.
-
Custom-Designed Glassy Carbon Tips for Atomic Force Microscopy.Micromachines (Basel). 2017 Sep 20;8(9):285. doi: 10.3390/mi8090285. Micromachines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30400475 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic-Dielectric Cantilevers for Atomic Force Microscopy.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 May 17;14(10):874. doi: 10.3390/nano14100874. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786830 Free PMC article.
-
Facile design of lidocaine-loaded polymeric hydrogel to persuade effects of local anesthesia drug delivery system: complete in vitro and in vivo toxicity analyses.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):1080-1092. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1931558. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34114924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bottomley L. A. Scanning probe microscopy. Anal. Chem. 70, 425–476 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Binnig G. & Rohrer H. Scanning tunneling microscopy. IBM J. Res. Dev. 44, 279–293 (2000).
-
- Binnig G., Quate C. F. & Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 930–933 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Bull M. S., Sullan R. M. A., Li H. & Perkins T. T. Improved single molecule force spectroscopy using micromachined cantilevers. ACS Nano 8, 4984–4995 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Li M., Tang H. X. & Roukes M. L. Ultra-sensitive NEMS-based cantilevers for sensing, scanned probe and very high-frequency applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 114–120 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

