Membrane Topology and Structural Insights into the Peptide Pheromone Receptor ComD, A Quorum-Sensing Histidine Protein Kinase of Streptococcus mutans
- PMID: 27199267
- PMCID: PMC4873836
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26502
Membrane Topology and Structural Insights into the Peptide Pheromone Receptor ComD, A Quorum-Sensing Histidine Protein Kinase of Streptococcus mutans
Abstract
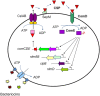
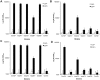
Quorum sensing activation by signal pheromone (CSP) in Streptococcus mutans depends on the membrane-associated receptor ComD, which senses the signal and triggers the signaling cascade for bacteriocin production and other cell density-dependent activities. However, the mechanism of the signal recognition via the ComD receptor in this species is nearly unexplored. Here, we show that the membrane domain of the ComD protein forms six transmembrane segments with three extracellular loops, loopA, loopB and loopC. By structural and functional analyses of these extracellular loops, we demonstrate that both loopC and loopB are required for CSP recognition, while loopA plays little role in CSP detection. A deletion or substitution mutation of four residues NVIP in loopC abolishes CSP recognition for quorum sensing activities. We conclude that both loopC and loopB are required for forming the receptor and residues NVIP of loopC are essential for CSP recognition and quorum sensing activation in S. mutans.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Structure-Activity Relationships of the Competence Stimulating Peptide in Streptococcus mutans Reveal Motifs Critical for Membrane Protease SepM Recognition and ComD Receptor Activation.ACS Infect Dis. 2018 Sep 14;4(9):1385-1394. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00115. Epub 2018 Jul 23. ACS Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29990430 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and functional studies of a potent modified quorum-sensing peptide and a two-peptide bacteriocin in Streptococcus mutans.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Sep;61(5):1322-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05312.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16925560
-
Inhibiting effects of fructanase on competence-stimulating peptide-dependent quorum sensing system in Streptococcus mutans.J Infect Chemother. 2017 Sep;23(9):634-641. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Jul 17. J Infect Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28729051
-
Quorum sensing and biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:178-88. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792689 Review.
-
Toward understanding the signals of bacteriocin production by Streptococcus spp. and their importance in current applications.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jan 4;37(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02973-5. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33394178 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the Vocabulary of Peptide Signals in Streptococcus mutans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jun 6;9:194. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00194. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31245303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ClpP is required for proteolytic regulation of type II toxin-antitoxin systems and persister cell formation in Streptococcus mutans.Access Microbiol. 2019 Sep 25;1(8):e000054. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000054. eCollection 2019. Access Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 32974554 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Membrane Protein Topology Using pho-lac Reporter Fusions.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2715:181-195. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3445-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37930528
-
Development and utilization of peptide-based quorum sensing modulators in Gram-positive bacteria.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Sep 30;18(37):7273-7290. doi: 10.1039/d0ob01421d. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32914160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Conserved Quorum Sensing Signals in Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 30;10(12):2386. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122386. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stock A. M., Robinson V. L. & Goudreau P. N. Two-component signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69, 183–215 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Grebe T. W. & Stock J. B. The histidine protein kinase superfamily. p139-227. In Poole R. K. (ed) Advances in microbial physiology. (Academic Press, UK, 1999). - PubMed
-
- Jung K., Fried L., Behr S. & Heermann R. Histidine kinases and response regulators in networks. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 15, 118–124 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

