Intrahippocampal Administration of Ibotenic Acid Induced Cholinergic Dysfunction via NR2A/NR2B Expression: Implications of Resveratrol against Alzheimer Disease Pathophysiology
- PMID: 27199654
- PMCID: PMC4844917
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00028
Intrahippocampal Administration of Ibotenic Acid Induced Cholinergic Dysfunction via NR2A/NR2B Expression: Implications of Resveratrol against Alzheimer Disease Pathophysiology
Abstract
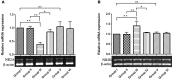
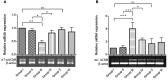
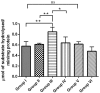
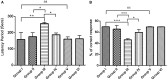
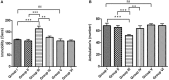
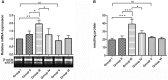
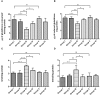
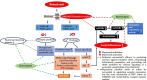
Although several drugs revealed moderate amelioration of symptoms, none of them have sufficient potency to prevent or reverse the progression toward Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. Resveratrol (RSV), a polyphenolic compound has shown an outstanding therapeutic effect on a broad spectrum of diseases like age-associated neurodegeneration, inflammation etc. The present study was thus conducted to assess the therapeutic efficacy of RSV in ameliorating the deleterious effects of Ibotenic acid (IBO) in male Wistar rats. Stereotactic intrahippocampal administration of IBO (5 μg/μl) lesioned rats impairs cholinergic transmission, learning and memory performance that is rather related to AD and thus chosen as a suitable model to understand the drug efficacy in preventing AD pathophysiology. Since IBO is an agonist of glutamate, it is expected to exhibit an excitotoxic effect by altering glutamatergic receptors like NMDA receptor. The current study displayed significant alterations in the mRNA expression of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptors, and further it is surprising to note that cholinergic receptors decreased in expression particularly α7-nAChR with increased m1AChR. RSV administration (20 mg/kg body weight, i.p.) significantly reduced these changes in IBO induced rats. Glutamatergic and cholinergic receptor alterations were associated with significant changes in the behavioral parameters of rats induced by IBO. While RSV improved spatial learning performance, attenuated immobility, and improvised open field activity in IBO induced rats. NR2B activation in the present study might mediate cell death through oxidative stress that form the basis of abnormal behavioral pattern in IBO induced rats. Interestingly, RSV that could efficiently encounter oxidative stress have significantly decreased stress markers viz., nitrite, PCO, and MDA levels by enhancing antioxidant status. Histopathological analysis displayed significant reduction in the hippocampal pyramidal layer thickness and live neurons in IBO induced rats, with slight pathological changes in the entorhinal cortex (EC) of rat brain, which was prevented on RSV administration. Our study thus concludes that RSV administration significantly ameliorated the deleterious effects in the IBO lesioned rat model for AD by alleviating cholinergic pathways, reducing oxidative stress and thereby improving spatial memory.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; NMDAR; acetylcholine receptors; hippocampus; ibotenic acid; memory; resveratrol.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Time-dependent effect of oligomeric amyloid-β (1-42)-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurol Res. 2019 Feb;41(2):139-150. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1544745. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Neurol Res. 2019. PMID: 30453864
-
Icariside II ameliorates ibotenic acid-induced cognitive impairment and apoptotic response via modulation of MAPK pathway in rats.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 1;41:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.01.025. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29519323
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A and NR2B messenger RNA levels are altered in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurol Sci. 2002 Aug 15;200(1-2):11-8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(02)00087-4. J Neurol Sci. 2002. PMID: 12127670
-
[Selective stimulations and lesions of the rat brain nuclei as the models for research of the human sleep pathology mechanisms].Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2011;(51):85-97. Glas Srp Akad Nauka Med. 2011. PMID: 22165729 Review. Serbian.
-
Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol in Alzheimer's disease.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2020 Jan 1;12(1):139-149. doi: 10.2741/E863. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2020. PMID: 31585875 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Foods: An Approach to Modulate Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2020 Oct 23;9(11):2347. doi: 10.3390/cells9112347. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33114170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ellagic acid improves the symptoms of early-onset Alzheimer's disease: Behavioral and physiological correlates.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 7;10(18):e37372. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37372. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39309887 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of resveratrol, curcumin, berberine and other nutraceuticals on aging, cancer development, cancer stem cells and microRNAs.Aging (Albany NY). 2017 Jun 12;9(6):1477-1536. doi: 10.18632/aging.101250. Aging (Albany NY). 2017. PMID: 28611316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-transgenic rodent models of Alzheimer's disease for preclinical research: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 14;52(1):456. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10549-5. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40366433 Review.
-
A resveratrol derivative modulates TRH and TRH-like peptide expression throughout the brain and peripheral tissues of male rats.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022 Sep;5(5):e356. doi: 10.1002/edm2.356. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35875858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auerbach J. M., Segal M. (1994). A novel cholinergic induction of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 2034–2040. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

