Abscisic Acid and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants
- PMID: 27200044
- PMCID: PMC4855980
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00571
Abscisic Acid and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants
Abstract
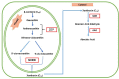
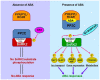
Abiotic stress is a primary threat to fulfill the demand of agricultural production to feed the world in coming decades. Plants reduce growth and development process during stress conditions, which ultimately affect the yield. In stress conditions, plants develop various stress mechanism to face the magnitude of stress challenges, although that is not enough to protect them. Therefore, many strategies have been used to produce abiotic stress tolerance crop plants, among them, abscisic acid (ABA) phytohormone engineering could be one of the methods of choice. ABA is an isoprenoid phytohormone, which regulates various physiological processes ranging from stomatal opening to protein storage and provides adaptation to many stresses like drought, salt, and cold stresses. ABA is also called an important messenger that acts as the signaling mediator for regulating the adaptive response of plants to different environmental stress conditions. In this review, we will discuss the role of ABA in response to abiotic stress at the molecular level and ABA signaling. The review also deals with the effect of ABA in respect to gene expression.
Keywords: ABA signaling; abiotic stress; abscisic acid; gene expression; phytohormone.
Figures
References
-
- Agrawal G. K., Tamogami S., Iwahashi H., Agrawal V. P., Rakwal R. (2003). Transient regulation of jasmonic acid-inducible rice MAP kinase gene (OsBWMK1) by diverse biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 41 355–361. 10.1016/S0981-9428(03)00030-5 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

