Unraveling Aspects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Mediated Enhanced Production of Rice under Biotic Stress of Rhizoctonia solani
- PMID: 27200058
- PMCID: PMC4858605
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00587
Unraveling Aspects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Mediated Enhanced Production of Rice under Biotic Stress of Rhizoctonia solani
Abstract
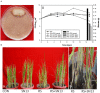
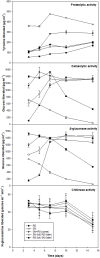
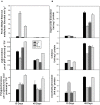
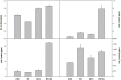
Rhizoctonia solani is a necrotrophic fungi causing sheath blight in rice leading to substantial loss in yield. Excessive and persistent use of preventive chemicals raises human health and environment safety concerns. As an alternative, use of biocontrol agents is highly recommended. In the present study, an abiotic stress tolerant, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (SN13) is demonstrated to act as a biocontrol agent and enhance immune response against R. solani in rice by modulating various physiological, metabolic, and molecular functions. A sustained tolerance by SN13 primed plant over a longer period of time, post R. solani infection may be attributed to several unconventional aspects of the plants' physiological status. The prolonged stress tolerance observed in presence of SN13 is characterized by (a) involvement of bacterial mycolytic enzymes, (b) sustained maintenance of elicitors to keep the immune system induced involving non-metabolizable sugars such as turanose besides the known elicitors, (c) a delicate balance of ROS and ROS scavengers through production of proline, mannitol, and arabitol and rare sugars like fructopyranose, β-D-glucopyranose and myoinositol and expression of ferric reductases and hypoxia induced proteins, (d) production of metabolites like quinazoline and expression of terpene synthase, and (e) hormonal cross talk. As the novel aspect of biological control this study highlights the role of rare sugars, maintenance of hypoxic conditions, and sucrose and starch metabolism in B. amyloliquefaciens (SN13) mediated sustained biotic stress tolerance in rice.
Keywords: B. amyloliquefaciens; Rhizoctonia solani; biological control; plant growth promotion; sheath blight.
Figures

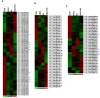

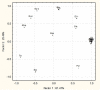
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

