Dissecting miRNAs in Wheat D Genome Progenitor, Aegilops tauschii
- PMID: 27200073
- PMCID: PMC4855405
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00606
Dissecting miRNAs in Wheat D Genome Progenitor, Aegilops tauschii
Abstract
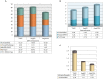
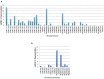
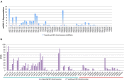
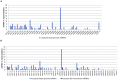
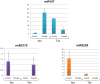
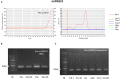
As the post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression, microRNAs or miRNAs comprise an integral part of understanding how genomes function. Although miRNAs have been a major focus of recent efforts, miRNA research is still in its infancy in most plant species. Aegilops tauschii, the D genome progenitor of bread wheat, is a wild diploid grass exhibiting remarkable population diversity. Due to the direct ancestry and the diverse gene pool, A. tauschii is a promising source for bread wheat improvement. In this study, a total of 87 Aegilops miRNA families, including 51 previously unknown, were computationally identified both at the subgenomic level, using flow-sorted A. tauschii 5D chromosome, and at the whole genome level. Predictions at the genomic and subgenomic levels suggested A. tauschii 5D chromosome as rich in pre-miRNAs that are highly associated with Class II DNA transposons. In order to gain insights into miRNA evolution, putative 5D chromosome miRNAs were compared to its modern ortholog, Triticum aestivum 5D chromosome, revealing that 48 of the 58 A. tauschii 5D miRNAs were conserved in orthologous T. aestivum 5D chromosome. The expression profiles of selected miRNAs (miR167, miR5205, miR5175, miR5523) provided the first experimental evidence for miR5175, miR5205 and miR5523, and revealed differential expressional changes in response to drought in different genetic backgrounds for miR167 and miR5175. Interestingly, while miR5523 coding regions were present and expressed as pre-miR5523 in both T. aestivum and A. tauschii, the expression of mature miR5523 was observed only in A. tauschii under normal conditions, pointing out to an interference at the downstream processing of pre-miR5523 in T. aestivum. Overall, this study expands our knowledge on the miRNA catalog of A. tauschii, locating a subset specifically to the 5D chromosome, with ample functional and comparative insight which should contribute to and complement efforts to develop drought tolerant wheat varieties.
Keywords: Aegilops tauschii; D genome; Triticum aestivum; drought; microRNA; next generation sequencing.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

