Study on the Mechanism Underlying the Regulation of the NMDA Receptor Pathway in Spinal Dorsal Horns of Visceral Hypersensitivity Rats by Moxibustion
- PMID: 27200098
- PMCID: PMC4855029
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/3174608
Study on the Mechanism Underlying the Regulation of the NMDA Receptor Pathway in Spinal Dorsal Horns of Visceral Hypersensitivity Rats by Moxibustion
Abstract
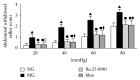
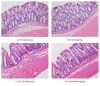
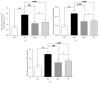
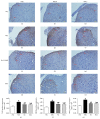
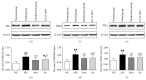
Visceral hypersensitivity is enhanced in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients. Treatment of IBS visceral pain by moxibustion methods has a long history and rich clinical experience. In the clinic, moxibustion on the Tianshu (ST25) and Shangjuxu (ST37) acupoints can effectively treat bowel disease with visceral pain and diarrhea symptoms. To investigate the regulatory function of moxibustion on the Tianshu (ST25) and Shangjuxu (ST37) acupoints on spinal cord NR1, NR2B, and PKCε protein and mRNA expression in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) visceral hypersensitivity rats, we did some research. In the study, we found that moxibustion effectively relieved the IBS visceral hyperalgesia status of rats. Analgesic effect of moxibustion was similar to intrathecal injection of Ro 25-6981. The expression of NR1, NR2B, and PKCε in the spinal dorsal horns of IBS visceral hyperalgesia rats increased. Moxibustion on the Tianshu and Shangjuxu acupoints might inhibit the visceral hypersensitivity, simultaneously decreasing the expression of NR1, NR2B, and PKCε in spinal cord of IBS visceral hyperalgesia rats. Based on the above experimental results, we hypothesized NR1, NR2B, and PKCε of spinal cord could play an important role in moxibustion inhibiting the process of central sensitization and visceral hyperalgesia state.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spinal cord astrocyte P2X7Rs mediate the inhibitory effect of electroacupuncture on visceral hypersensitivity of rat with irritable bowel syndrome.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):43-53. doi: 10.1007/s11302-021-09830-6. Epub 2022 Apr 7. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35389158 Free PMC article.
-
Moxibustion ameliorates visceral hypersensitivity by regulating hypothalamus-spinal cord-colon axis in rats with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024 Jan 25;49(1):47-56. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20221092. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024. PMID: 38239138 Chinese, English.
-
[Effects of mild moxibustion on visceral hypersensitivity via SCF/c-kit signaling pathway in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome rats with syndrome of liver-qi stagnation and spleen deficiency].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024 Sept 25;49(9):924-932. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20230280. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024. PMID: 39401829 Chinese.
-
Mechanisms underlying the analgesic effect of moxibustion on visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome: a review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:895914. doi: 10.1155/2014/895914. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 25093032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture-moxibustion in treating irritable bowel syndrome: how does it work?World J Gastroenterol. 2014 May 28;20(20):6044-54. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6044. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24876727 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The efficacy and neural mechanism of acupuncture therapy in the treatment of visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome.Front Neurosci. 2023 Sep 4;17:1251470. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1251470. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37732301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2X7 and P2Y1 receptors in DRG mediate electroacupuncture to inhibit peripheral sensitization in rats with IBS visceral pain.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Jun 26. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-10028-9. Online ahead of print. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38922475
-
Moxibustion as an Adjuvant Therapy for Cancer Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pain Res. 2023 Feb 17;16:515-525. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S396696. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 36824500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture and Moxibustion Modulate the BDNF and TrkB Expression in the Colon and Dorsal Root Ganglia of IBS Rats with Visceral Hypersensitivity.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 28;2021:8137244. doi: 10.1155/2021/8137244. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34621325 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Electroacupuncture at Different Acupoints on the Expression of NMDA Receptors in ACC and Colon in IBS Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Feb 3;2019:4213928. doi: 10.1155/2019/4213928. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30854008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang M. Progress in the studies of visceral hypersensitivity-central sensitization. Chongqing Medicine. 2009;38(15):1958–1960.
-
- Wang Y. M., Xia Y. Y., Min Y. Voltage-gated calcium channel as a target for new analgesic drugs. World Clinical Drugs. 2010;31(7):433–437.
-
- Shi J., Liu M., Lan L., et al. Application of moxibustion in the treatment of functional gastrointestinal diseases. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2012;53(18, article 1605)
-
- Wang S. Y., Chen X., Gao Q. G. Clinical observation of treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) using moxibustion. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion. 2003;19(10):43–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

