Modified Nucleoside Triphosphates for In-vitro Selection Techniques
- PMID: 27200340
- PMCID: PMC4854868
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2016.00018
Modified Nucleoside Triphosphates for In-vitro Selection Techniques
Abstract
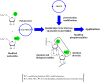
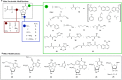
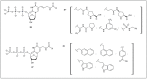
The development of SELEX (Selective Enhancement of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment) provides a powerful tool for the search of functional oligonucleotides with the ability to bind ligands with high affinity and selectivity (aptamers) and for the discovery of nucleic acid sequences with diverse enzymatic activities (ribozymes and DNAzymes). This technique has been extensively applied to the selection of natural DNA or RNA molecules but, in order to improve chemical and structural diversity as well as for particular applications where further chemical or biological stability is necessary, the extension of this strategy to modified oligonucleotides is desirable. Taking into account these needs, this review intends to collect the research carried out during the past years, focusing mainly on the use of modified nucleotides in SELEX and the development of mutant enzymes for broadening nucleoside triphosphates acceptance. In addition, comments regarding the synthesis of modified nucleoside triphosphate will be briefly discussed.
Keywords: DNAzymes; SELEX; aptamers; functional oligonucleotides; modified nucleotides; ribozymes.
Figures
References
-
- Battersby T. R., Ang D. N., Burgstaller P., Jurczyk S. C., Bowser M. T., Buchanan D. D., et al. (1999). Quantitative analysis of receptors for adenosine nucleotides obtained via in vitro selection from a library incorporating a cationic nucleotide analog. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 9781–9789. 10.1021/ja9816436 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

