Insulin decreases atherosclerosis by inducing endothelin receptor B expression
- PMID: 27200419
- PMCID: PMC4869734
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.86574
Insulin decreases atherosclerosis by inducing endothelin receptor B expression
Abstract
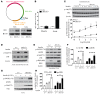
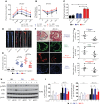
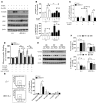
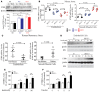
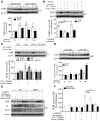
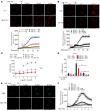
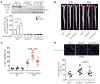
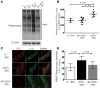
Endothelial cell (EC) insulin resistance and dysfunction, caused by diabetes, accelerates atherosclerosis. It is unknown whether specifically enhancing EC-targeted insulin action can decrease atherosclerosis in diabetes. Accordingly, overexpressing insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS1) in the endothelia of Apoe-/- mice (Irs1/Apoe-/-) increased insulin signaling and function in the aorta. Atherosclerosis was significantly reduced in Irs1/ApoE-/- mice on diet-induced hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia. The mechanism of insulin's enhanced antiatherogenic actions in EC was related to remarkable induction of NO action, which increases endothelin receptor B (EDNRB) expression and intracellular [Ca2+]. Using the mice with knockin mutation of eNOS, which had Ser1176 mutated to alanine (AKI), deleting the only known mechanism for insulin to activate eNOS/NO pathway, we observed that IRS1 overexpression in the endothelia of Aki/ApoE-/- mice significantly decreased atherosclerosis. Interestingly, endothelial EDNRB expression was selectively reduced in intima of arteries from diabetic patients and rodents. However, endothelial EDNRB expression was upregulated by insulin via P13K/Akt pathway. Finally EDNRB deletion in EC of Ldlr-/- and Irs1/Ldlr-/- mice decreased NO production and accelerated atherosclerosis, compared with Ldlr-/- mice. Accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetes may be reduced by improving insulin signaling selectively via IRS1/Akt in the EC by inducing EDNRB expression and NO production.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpressing IRS1 in Endothelial Cells Enhances Angioblast Differentiation and Wound Healing in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance.Diabetes. 2016 Sep;65(9):2760-71. doi: 10.2337/db15-1721. Epub 2016 May 23. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27217486 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cells Induced Progenitors Into Brown Fat to Reduce Atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 2022 Jul 8;131(2):168-183. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319582. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35642564 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside improves endothelial function and alleviates atherosclerosis by activating a mitochondria-related AMPK/PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway.Vascul Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;72:141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Vascul Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26187353
-
Selective Insulin Resistance and the Development of Cardiovascular Diseases in Diabetes: The 2015 Edwin Bierman Award Lecture.Diabetes. 2016 Jun;65(6):1462-71. doi: 10.2337/db16-0152. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27222390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective Insulin Resistance in the Kidney.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5825170. doi: 10.1155/2016/5825170. Epub 2016 May 9. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27247938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Cognitive Function and Retinal Neural and Vascular Structure in Type 1 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Mar 25;106(4):1139-1149. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa921. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33378459 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Mystery of Insulin Resistance: From Principle Mechanistic Insights and Consequences to Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2770. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062770. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpressing IRS1 in Endothelial Cells Enhances Angioblast Differentiation and Wound Healing in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance.Diabetes. 2016 Sep;65(9):2760-71. doi: 10.2337/db15-1721. Epub 2016 May 23. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27217486 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: The Changing Panorama of Diabetes Outcomes: Novel Complications and Novelties in Classical Complication.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 13;12:816481. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.816481. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35095775 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protective Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid on the Glomerular Endothelium via Inhibition of EndMT in Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Dec 24;2021:2182225. doi: 10.1155/2021/2182225. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 34977254 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

