Effect of acute lithium administration on penile erection: involvement of nitric oxide system
- PMID: 27200425
- PMCID: PMC4869162
Effect of acute lithium administration on penile erection: involvement of nitric oxide system
Abstract
Background: Lithium has been the treatment of choice for bipolar disorder (BD) for many years. Although erectile dysfunction is a known adverse effect of this drug, the mechanism of action by which lithium affects erectile function is still unknown.
Objective: The aim was to investigate the possible involvement of nitric oxide (NO) in modulatory effect of lithium on penile erection (PE). We further evaluated the possible role of Sildenafil in treatment of lithium-induced erectile dysfunction.
Materials and methods: Erectile function was determined using rat model of apomorphine-induced erections. For evaluating the effect of lithium on penile erection, rats received intraperitoneal injection of graded doses of lithium chloride 30 mins before subcutaneous injection of apomorphine. To determine the possible role of NO pathway, sub-effective dose of N (G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor, was administered 15 min before administration of sub-effective dose of lithium chloride. In other separate experimental groups, sub- effective dose of the nitric oxide precursor, L-arginine, or Sildenafil was injected into the animals 15 min before administration of a potent dose of lithium. 30 min after administration of lithium chloride, animals were assessed in apomorphine test. Serum lithium levels were measured 30 min after administration of effective dose of lithium.
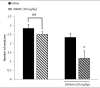
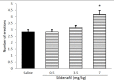
Results: Lithium at 50 and 100 mg/kg significantly decreased number of PE (p<0.001), whereas at lower doses (5, 10 and 30 mg/kg) had no effect on apomorphine induced PE. The serum Li+ level of rats receiving 50 mg/kg lithium was 1±0.15 mmol/L which is in therapeutic range of lithium. The inhibitory effect of Lithium was blocked by administration of sub-effective dose of nitric oxide precursor L-arginine (100 mg/kg) (p<0.001) and sildenafil (3.5 mg/kg) (p<0.001) whereas pretreatment with a low and sub-effective dose of L-NAME (10mg/kg) potentiated sub-effective dose of lithium, (p<0.001).
Conclusion: These results suggest acute treatments with lithium cause erectile dysfunction in an in-vivo rat model. Furthermore it seems that the NO pathway might play role in erectile dysfunction associated with lithium treatment. Findings also suggest that Sildenafil may be effective in treatment of lithium-associated erectile dysfunction.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; Lithium; Nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lithium and Erectile Dysfunction: An Overview.Cells. 2022 Jan 5;11(1):171. doi: 10.3390/cells11010171. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic inhibition of nitric-oxide synthase induces hypertension and erectile dysfunction in the rat that is not reversed by sildenafil.BJU Int. 2010 Jul;106(1):78-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.09104.x. Epub 2009 Dec 11. BJU Int. 2010. PMID: 20002674
-
Lithium chloride disrupts consolidation of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in male mice: the nitric oxide/cyclic GMP signaling pathway.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Jun 1;219(2):240-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.01.014. Epub 2011 Jan 15. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21241742
-
Intracavernosal sildenafil facilitates penile erection independent of the nitric oxide pathway.J Androl. 2001 Jul-Aug;22(4):623-8. J Androl. 2001. PMID: 11451359
-
New treatment options for erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2004;64(23):2667-88. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464230-00004. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15537369 Review.
Cited by
-
Lithium and zinc levels along with oxidative status in myocardial infarction: A case-control study.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 7;9(11):e21875. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21875. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027575 Free PMC article.
-
Premature Ejaculation after Lithium Treatment in a Patient with Bipolar Disorder.Case Rep Psychiatry. 2023 Jan 9;2023:6156023. doi: 10.1155/2023/6156023. eCollection 2023. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36655208 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium and Erectile Dysfunction: An Overview.Cells. 2022 Jan 5;11(1):171. doi: 10.3390/cells11010171. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cade JF. Lithium salts in the treatment of psychotic excitement. Med J Aust. 1949;2:349–352. - PubMed
-
- Ghadirian AM, Annable L, Belanger MC. Lithium, benzodiazepines, and sexual function in bipolar patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1992;149:801–805. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin GM. Evidence-based guidelines for treating bipolar disorder: revised second edition-recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol. 2009;23:346–388. - PubMed
-
- Young AH, Hammond JM. Lithium in mood disorders: increasing evidence base, declining use? Br J Psychiatry. 2007;191:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Frye MA, Yatham L, Ketter TA, Goldberg J, Suppes T, Calabrese JR, et al. Depressive relapse during lithium treatment associated with increased serum thyroid-stimulating hormone: results from two placebo-controlled bipolar I maintenance studies. Acta Psychiatrica Scand. 2009;120:10–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
