Age, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression and function in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 27203211
- PMCID: PMC5094941
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9398
Age, serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression and function in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
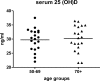
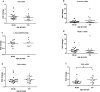
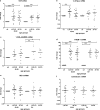
The relationship between age, vitamin D status, expression and functionality of the vitamin D receptor (VDR), and key genes in the vitamin D pathway in immune cells is unclear. We enrolled adults 50 to 69 years old (20 subjects) and 70+ (20 subjects) and measured: 1) 25(OH)D levels by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry; and 2) mRNA expression of VDR, 1α-OHase, 1,25D3-MARRS, TREM-1, cathelicidin, RIG-I, and interferon-β by qRT-PCR. Mean serum 25(OH)D was 30 ± 4 ng/mL and was not associated with age. Baseline expression of VDR, 1α-OHase, 1,25D3-MARRS, TREM-1, and RIG-I also did not differ by age; IFN-β expression, however, was higher in the 70+ year old group. 25(OH)D3- and 1,25(OH)2D3-induced VDR, TREM-1 and cathelicidin expression were similar between age groups, as was LPS-induced expression of VDR and of 1α-OHase. Ligand-induced 1,25D3-MARRS expression was higher in subjects ≥ 70 years. Serum 25(OH)D was inversely associated with LPS-stimulated VDR expression and with baseline or vitamin D-induced TREM-1 expression, adjusting for age, self-rated health, and functional status. In healthy adults ≥ 50 years, the expression and functionality of the VDR, 1α-OHase and key vitamin D pathway genes were not consistently associated with age.
Keywords: 1α-hydroxylase; Gerotarget; PBMC; mRNA expression; vitamin D; vitamin D receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors, MM, MT, SMS, AJR, WGD, P-YC, EAB, DKS and SS declare no conflict of interest. HKT has received research funding from Sanofi Pasteur, MedImmune, and Gilead; and she serves on Advisory Boards for Teva Pharmaceuticals and MedImmune. MES has received research funding from MedImmune. MRG receives research funding from MedImmune. LAC is an employee of Abbott Nutrition.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3 level and expression of vitamin d receptor and cathelicidin in pulmonary tuberculosis.J Clin Immunol. 2009 Jul;29(4):470-8. doi: 10.1007/s10875-009-9277-9. Epub 2009 Feb 14. J Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19219539
-
Vitamin D Receptor Gene Expression and Function in a South African Population: Ethnicity, Vitamin D and FokI.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 21;8(6):e67663. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067663. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23805323 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D-induced up-regulation of human keratinocyte cathelicidin anti-microbial peptide expression involves retinoid X receptor α.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Nov;366(2):353-362. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2449-z. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27357804
-
Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with increased bladder cancer risk: A systematic review and evidence of a potential mechanism.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Apr;188:134-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Jan 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30654104
-
The vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: molecular actions and disease states.J Endocrinol. 1997 Sep;154 Suppl:S57-73. J Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9379138 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and VDR Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Leukemia Patients and Healthy Subjects in Central Kazakhstan.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 26;12(5):1229. doi: 10.3390/nu12051229. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32357551 Free PMC article.
-
1,25-(OH)2D3/Vitamin D receptor alleviates systemic lupus erythematosus by downregulating Skp2 and upregulating p27.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Dec 10;17(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0488-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31823770 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Nutritional Factors on Immunological Outcomes.Front Immunol. 2021 May 31;12:665968. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665968. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34135894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphisms in vitamin D receptor genes and its relation with susceptibility to brucellosis: a case-control study.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Mar;50(3):2077-2083. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08195-2. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36542233
-
Fluorescence Analysis of Vitamin D Receptor Status of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCS) in Breast Cancer: From Cell Models to Metastatic Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 20;18(6):1318. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061318. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28632174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, VanMeurs JB, Pols HA, VanLeeuwen JP. Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene. 2004;338:143–156. - PubMed
-
- Wolden-Kirk H, Gysemans C, Verstuyf A, Mathieu C. Extraskeletal effects of vitamin D. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 2012;41:571–594. - PubMed
-
- Baeke F, Takiishi T, Kork H, Gysemans C, Mathieu C. Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010;10:482–496. - PubMed
-
- Hewison M. Vitamin D and immune function: an overview. Proc Nutr Soc. 2011;71:50–61. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Rodriguez L, Lopez-Hoyos M, Garcia-Unzueta M, Amado JA, Cacho PM, Martinez-Taboada VM. Age and low levels of circulating vitamin D are associated with impaired innate immune function. J Leuko Biol. 2012;91:829–838. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

