Antimicrobial Functions of Lactoferrin Promote Genetic Conflicts in Ancient Primates and Modern Humans
- PMID: 27203426
- PMCID: PMC4874600
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006063
Antimicrobial Functions of Lactoferrin Promote Genetic Conflicts in Ancient Primates and Modern Humans
Abstract
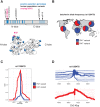
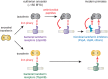
Lactoferrin is a multifunctional mammalian immunity protein that limits microbial growth through sequestration of nutrient iron. Additionally, lactoferrin possesses cationic protein domains that directly bind and inhibit diverse microbes. The implications for these dual functions on lactoferrin evolution and genetic conflicts with microbes remain unclear. Here we show that lactoferrin has been subject to recurrent episodes of positive selection during primate divergence predominately at antimicrobial peptide surfaces consistent with long-term antagonism by bacteria. An abundant lactoferrin polymorphism in human populations and Neanderthals also exhibits signatures of positive selection across primates, linking ancient host-microbe conflicts to modern human genetic variation. Rapidly evolving sites in lactoferrin further correspond to molecular interfaces with opportunistic bacterial pathogens causing meningitis, pneumonia, and sepsis. Because microbes actively target lactoferrin to acquire iron, we propose that the emergence of antimicrobial activity provided a pivotal mechanism of adaptation sparking evolutionary conflicts via acquisition of new protein functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Haldane J. Disease and evolution. La Ricerca Scientifica Supplemento. 1949;: 1–11.
-
- Van Valen L. A new evolutionary law. Evol Theory. 1973;1: 1–30.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

