Efficacy of CD46-targeting chimeric Ad5/35 adenoviral gene therapy for colorectal cancers
- PMID: 27203670
- PMCID: PMC5122383
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9427
Efficacy of CD46-targeting chimeric Ad5/35 adenoviral gene therapy for colorectal cancers
Abstract
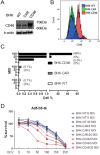
CD46 is a complement inhibitor membrane cofactor which also acts as a receptor for various microbes, including species B adenoviruses (Ads). While most Ad gene therapy vectors are derived from species C and infect cells through coxsackie-adenovirus receptor (CAR), CAR expression is downregulated in many cancer cells, resulting inefficient Ad-based therapeutics. Despite a limited knowledge on the expression status of many cancer cells, an increasing number of cancer gene therapy studies include fiber-modified Ad vectors redirected to the more ubiquitously expressed CD46. Since our finding from tumor microarray indicate that CD46 was overexpressed in cancers of the prostate and colon, fiber chimeric Ad5/35 vectors that have infection tropism for CD46 were employed to demonstrate its efficacy in colorectal cancers (CRC). CD46-overexpressed cells showed a significantly higher response to Ad5/35-GFP and to Ad5/35-tk/GCV. While CRC cells express variable levels of CD46, CD46 expression was positively correlated with Ad5/35-mediated GFP fluorescence and accordingly its cell killing. Injection of Ad5/35-tk/GCV caused much greater tumor-suppression in mice bearing CD46-overexpressed cancer xenograft compared to mock group. Analysis of CRC samples revealed that patients with positive CD46 expression had a higher survival rate (p=0.031), carried tumors that were well-differentiated, but less invasive and metastatic, and with a low T stage (all p<0.05). Taken together, our study demonstrated that species B-based adenoviral gene therapy is a suitable approach for generally CD46-overexpressed CRC but would require careful consideration preceding CD46 analysis and categorizing CRC patients.
Keywords: CD46; adenovirus; colorectal cancer; gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeting CD46 Enhances Anti-Tumoral Activity of Adenovirus Type 5 for Bladder Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 10;19(9):2694. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092694. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30201920 Free PMC article.
-
A novel fiber chimeric conditionally replicative adenovirus-Ad5/F35 for tumor therapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2017 Nov 2;18(11):833-840. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1395115. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017. PMID: 29144842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD46 represents a target for adenoviral gene therapy of malignant glioma.Hum Gene Ther. 2006 May;17(5):556-64. doi: 10.1089/hum.2006.17.556. Hum Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16716112
-
Enhanced antitumor efficacy of a novel fiber chimeric oncolytic adenovirus expressing p53 on hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2011 Aug 1;307(1):93-103. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.021. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21504839
-
Adenovirus vectors composed of subgroup B adenoviruses.Curr Gene Ther. 2007 Aug;7(4):229-38. doi: 10.2174/156652307781369137. Curr Gene Ther. 2007. PMID: 17969556 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel approach for breast cancer treatment: the multifaceted antitumor effects of rMeV-Hu191.Hereditas. 2024 Sep 28;161(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s41065-024-00337-9. Hereditas. 2024. PMID: 39342391 Free PMC article.
-
A Systems-Level Analysis Reveals Circadian Regulation of Splicing in Colorectal Cancer.EBioMedicine. 2018 Jul;33:68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.06.012. Epub 2018 Jun 21. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 29936137 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus Receptor Expression in Cancer and Its Multifaceted Role in Oncolytic Adenovirus Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 17;21(18):6828. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186828. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32957644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superior infectivity of the fiber chimeric oncolytic adenoviruses Ad5/35 and Ad5/3 over Ad5-delta-24-RGD in primary glioma cultures.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Dec 21;24:230-248. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.12.013. eCollection 2022 Mar 17. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 35071746 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of glioma by adenovirus KGHV500 encoding anti-p21Ras scFv and carried by cytokine-induced killer cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 May;246(10):1228-1238. doi: 10.1177/1535370220986769. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33535808 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Wilson JM. Adenoviruses as gene-delivery vehicles. The New England journal of medicine. 1996;334:1185–1187. - PubMed
-
- Hemminki A, Kanerva A, Liu B, Wang M, Alvarez RD, Siegal GP, Curiel DT. Modulation of coxsackie-adenovirus receptor expression for increased adenoviral transgene expression. Cancer research. 2003;63:847–853. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

