A novel multi-epitope recombined protein for diagnosis of human brucellosis
- PMID: 27206475
- PMCID: PMC4875615
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-016-1552-9
A novel multi-epitope recombined protein for diagnosis of human brucellosis
Abstract
Background: In epidemic regions of the world, brucellosis is a reemerging zoonosis with minimal mortality but is a serious public hygiene problem. Currently, there are various methods for brucellosis diagnosis, however few of them are available to be used to diagnose, especially for serious cross-reaction with other bacteria.
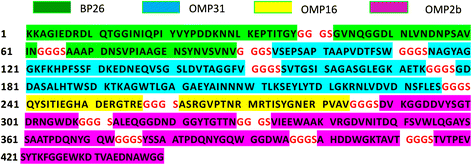
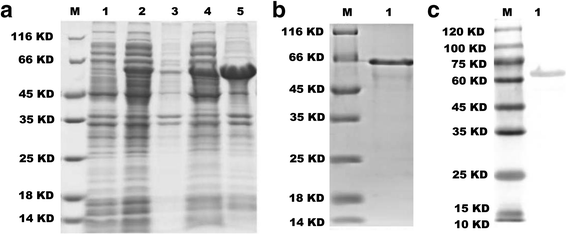
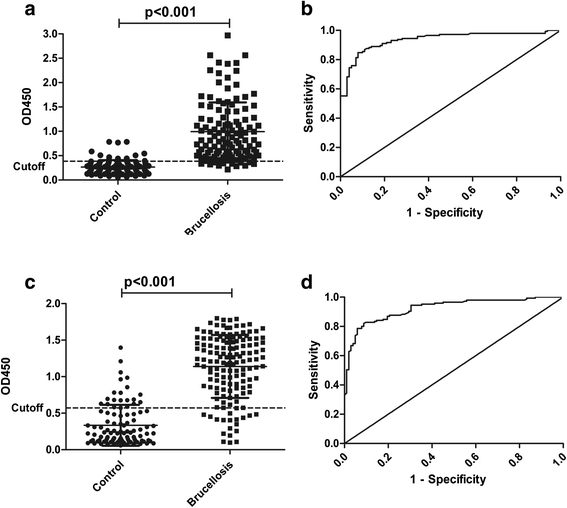
Method: To overcome this disadvantage, we explored a novel multi-epitope recombinant protein as human brucellosis diagnostic antigen. We established an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on this recombinant protein. 248 sera obtained from three different groups including patients with brucellosis (146 samples), non-brucellosis patients (82 samples), and healthy individuals (20 samples) were tested by indirect ELISA. To evaluate the assay, a receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and immunoblotting were carried out using these characterized serum samples.
Results: For this test, the area under the ROC curve was 0.9409 (95 % confidence interval, 0.9108 to 0.9709), and a sensitivity of 88.89 % and a specificity of 85.54 % was given with a cutoff value of 0.3865 from this ROC analysis. The Western blot results indicate that it is feasible to differentiate human brucellosis and non-brucellosis with the newly established method based on this recombinant protein.
Conclusion: Our results obtained high diagnostic accuracy of the ELISA assay which encourage the use of this novel recombinant protein as diagnostic antigen to implement serological diagnosis of brucellosis.
Keywords: Brucellosis; Diagnosis; Recombinant protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of an I-ELISA method based on multi-epitope fusion protein for diagnosis of human brucellosis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025 Apr 7;19(4):e0012995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012995. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2025. PMID: 40193524 Free PMC article.
-
Paper-based ELISA diagnosis technology for human brucellosis based on a multiepitope fusion protein.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Aug 17;15(8):e0009695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009695. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34403421 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of a Brucella multiepitope fusion protein based on bioinformatics and its application in serological diagnosis of human brucellosis.Sci Rep. 2025 May 31;15(1):19106. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04244-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40447804 Free PMC article.
-
[The value of culture and serological methods in the diagnosis of human brucellosis].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2008 Jan;42(1):185-95. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2008. PMID: 18444578 Review. Turkish.
-
Laboratory-based diagnosis of brucellosis--a review of the literature. Part I: Techniques for direct detection and identification of Brucella spp.Clin Lab. 2003;49(9-10):487-505. Clin Lab. 2003. PMID: 14572205 Review.
Cited by
-
Designing a multi-epitope vaccine candidate to combat MERS-CoV by employing an immunoinformatics approach.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 29;11(1):15431. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92176-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34326355 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Validation of a Multi-Epitope mRNA Vaccine Construct Against Human Monkeypox Virus (hMPXV) by Annotating Protein of Intracellular Mature Virus (IMV) Form of hMPXV.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 11;13(6):1439. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061439. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564159 Free PMC article.
-
Development of epitope-based peptide vaccine against novel coronavirus 2019 (SARS-COV-2): Immunoinformatics approach.J Med Virol. 2020 Jun;92(6):618-631. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25736. Epub 2020 Mar 5. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32108359 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-epitope vaccines: a promising strategy against tumors and viral infections.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Feb;15(2):182-184. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.92. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28890542 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Annotation of the Extracellular Enveloped Form of Monkeypox Virus for the Design, Screening, Validation, and Simulation of a Chimeric Vaccine Construct.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;14(7):830. doi: 10.3390/biology14070830. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zygmunt MS, Diaz MA, Teixeira-Gomes AP, Cloeckaert A. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the brucella melitensis sucb gene coding for an immunogenic dihydrolipoamide succinyltransferase homologous protein. Infect Immun. 2001;69:6537–40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6537-6540.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

