The supplemental use of infant formula in the context of universal breastfeeding practices in Western Nepal
- PMID: 27206532
- PMCID: PMC4875692
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-016-0602-1
The supplemental use of infant formula in the context of universal breastfeeding practices in Western Nepal
Abstract
Background: While the initiation of breastfeeding is universal in Nepal, little has been reported on formula feeding practices. This study aimed to report the prevalence of, and factors associated with, the use of infant formula as supplementary feeds in the Western region of Nepal.
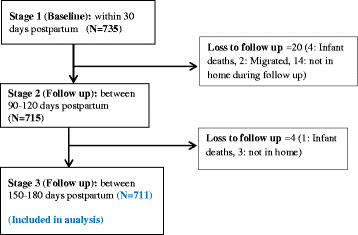
Methods: A community-based cohort study was conducted to collect infant feeding information among 735 postpartum mothers using structured questionnaires. Complete formula feeding data were collected from 711 women in the first, fourth and sixth month postpartum. Factors independently associated with formula feeding were investigated using multiple logistic regression.
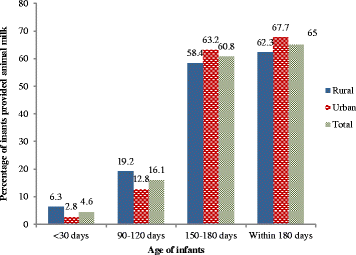
Results: All mothers were breastfeeding their infants at the time of recruitment. The prevalence of formula feeding was 7.5 % in the first month and 17 % in the sixth month. About a quarter of mothers (23.8 %) reported providing infant formula at least once during the first six months of life. Infant formula was used commonly as top-up food. Stepwise logistic regression showed that infants born to families residing in urban areas (adjusted odds ratio (aOR): 2.14; 95 % confidence interval (CI): 1.37 to 3.33), mothers with higher education (aOR: 2.08; 95 % CI: 1.14 to 3.80), and infants born by caesarean section (aOR: 1.96; 95 % CI: 1.21 to 3.18) were at greater risk of formula feeding.
Conclusion: The current findings indicate that health workers should support mothers to initiate and continue exclusive breastfeeding particularly after caesarean deliveries. Furthermore, urban health programs in Nepal should incorporate breastfeeding programs which discourage the unnecessary use of formula feeding. The marketing of formula milk should be monitored more vigilantly especially in the aftermath of the April 2015 earthquakes or other natural disasters.
Keywords: Baby formula; Breastfeeding; Cohort studies; Infant Formula; Infant food; Nepal; Urban Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and factors associated with prelacteal feeding in Western Nepal.Women Birth. 2016 Feb;29(1):12-7. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Women Birth. 2016. PMID: 26252964
-
Internet Use by First-Time Mothers for Infant Feeding Support.J Hum Lact. 2015 Aug;31(3):416-24. doi: 10.1177/0890334415584319. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Hum Lact. 2015. PMID: 25925637
-
Breastfeeding and Complementary Feeding Practices among HIV-Exposed Infants in Coastal Tanzania.J Hum Lact. 2016 Feb;32(1):112-22. doi: 10.1177/0890334415618412. Epub 2015 Nov 30. J Hum Lact. 2016. PMID: 26628498
-
Infant and young child feeding during natural disasters: A systematic integrative literature review.Women Birth. 2022 Nov;35(6):524-531. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2021.12.006. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Women Birth. 2022. PMID: 34996727
-
Breastfeeding and infant-mother interaction.Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999 Aug;88(430):1-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb01293.x. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10569216 Review.
Cited by
-
Formula feeding and associated factors among mothers with infants 0-6 months old in Mettu Town, Southwest Ethiopia.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 May 2;11(7):4136-4145. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3403. eCollection 2023 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37457147 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of breastfeeding education and support on predominant breastfeeding: Findings from a community-based prospective cohort study in Western Nepal.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 5;6(9):e1548. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1548. eCollection 2023 Sep. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37680209 Free PMC article.
-
Infant formula feeding and associated factors in Debre Berhan City: A community based cross-sectional study.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 6;10(18):e37594. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37594. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39309885 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of formula feeding among mothers with infants and young children in six Sub Sahara African countries: Multilevel analysis of data from demographic and health survey.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 26;19(12):e0311945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311945. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39724177 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Bottle-Feeding Practices in Kassala, Eastern Sudan: A Community-Based Study.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Feb 25;7(4):651-656. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.132. eCollection 2019 Feb 28. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30894930 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous