Fluoxetine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Implication in Depression
- PMID: 27207922
- PMCID: PMC5043644
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw037
Fluoxetine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Implication in Depression
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence indicates that NLRP3 inflammasome-induced inflammation plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of depression. Thus, inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation may offer a therapeutic benefit in the treatment of depression. Fluoxetine, a widely used antidepressant, has been shown to have potential antiinflammatory activity, but the underlying mechanisms remain obscure.
Methods: We used a chronic mild stress model and cultured primary macrophage/microglia to investigate the effects of fluoxetine on NLRP3 inflammasome and its underlying mechanisms.
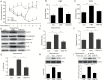
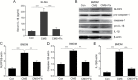
Results: We demonstrated that fluoxetine significantly suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation, subsequent caspase-1 cleavage, and interleukin-1β secretion in both peripheral macrophages and central microglia. We further found that fluoxetine reduced reactive oxygen species production, attenuated the phosphorylation of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, and inhibited the association of protein kinase with NLRP3. These data indicate that fluoxetine inhibits the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome via downregulating reactive oxygen species-protein kinase-NLRP3 signaling pathway. Correspondingly, in vivo data showed that fluoxetine also suppressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation in hippocampus and macrophages of chronic mild stress mice and alleviated chronic mild stress-induced depression-like behavior.
Conclusions: Our findings reveal that fluoxetine confers an antidepressant effect partly through inhibition of peripheral and central NLRP3 inflammasome activation and suggest the potential clinical use of fluoxetine in NLRP3 inflammasome-driven inflammatory diseases such as depression.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; depression; double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase; fluoxetine; reactive oxygen species.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metformin improves depressive-like symptoms in mice via inhibition of peripheral and central NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammation activation.Exp Brain Res. 2020 Nov;238(11):2549-2556. doi: 10.1007/s00221-020-05911-x. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Exp Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32870322
-
Tenuigenin protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Dec 20;14(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-1036-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 29262843 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates IL-1β-related inflammation in prefrontal cortex of depressive rats.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Oct;41:90-100. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.04.007. Epub 2014 May 22. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24859041
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediates Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Depression in Mice via Neuroinflammation.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Jan 20;18(8):pyv006. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv006. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25603858 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Its Role in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2020 Nov;45(11):2560-2572. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03121-z. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 32929691 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome in Translational Treatment of Nervous System Diseases: An Update.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 30;12:707696. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.707696. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34526897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the IL-6 Signaling Pathway in the Anti-Anhedonic Effect of the Antidepressant Agomelatine in the Chronic Mild Stress Model of Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12453. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012453. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293308 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin attenuated chronic social defeat stress induced depressive-like behaviors through suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome.Metab Brain Dis. 2019 Feb;34(1):319-329. doi: 10.1007/s11011-018-0342-z. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Metab Brain Dis. 2019. PMID: 30515710
-
Electro-Acupuncture Alleviates Chronic Unpredictable Stress-Induced Depressive- and Anxiety-Like Behavior and Hippocampal Neuroinflammation in Rat Model of Depression.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 May 31;11:149. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00149. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29946236 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Therapeutic Potential of Fluoxetine on Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer's Disease: Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 13;25(12):6542. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126542. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcocer-Gomez E, de Miguel M, Casas-Barquero N, Nunez-Vasco J, Sanchez-Alcazar JA, Fernandez-Rodriguez A, Cordero MD. (2014) NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in mononuclear blood cells from patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun 36:111–117. - PubMed
-
- Alcocer-Gomez E, Ulecia-Moron C, Marin-Aguilar F, Rybkina T, Casas-Barquero N, Ruiz-Cabello J, Ryffel B, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Bullon P, Sanchez-Alcazar JA, Carrion AM, Cordero MD. (2015) Stress-Induced depressive behaviors require a functional NLRP3 inflammasome. Mol Neurobiol 2015 Sep 11. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A, Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks BG, Fitzgerald KA, Hornung V, Latz E. (2009) Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol 183:787–791. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

