Variants of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin Member 4 in Childhood Atrioventricular Block
- PMID: 27207958
- PMCID: PMC4889160
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001625
Variants of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin Member 4 in Childhood Atrioventricular Block
Abstract
Background: Transient receptor potential melastatin member 4 (TRPM4) is a nonselective cation channel. TRPM4 mutations have been linked to cardiac conduction disease and Brugada syndrome. The mechanisms underlying TRPM4-dependent conduction slowing are not fully understood. The aim of this study was to characterize TRPM4 genetic variants found in patients with congenital or childhood atrioventricular block.
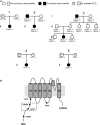
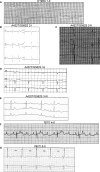
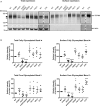
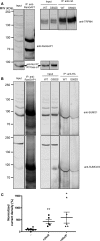
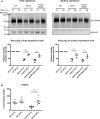
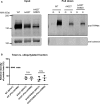
Methods and results: Ninety-one patients with congenital or childhood atrioventricular block were screened for candidate genes. Five rare TRPM4 genetic variants were identified and investigated. The variants were expressed heterologously in HEK293 cells. Two of the variants, A432T and A432T/G582S, showed decreased expression of the protein at the cell membrane; inversely, the G582S variant showed increased expression. Further functional characterization of these variants using whole-cell patch-clamp configuration showed a loss of function and a gain of function, respectively. We hypothesized that the observed decrease in expression was caused by a folding and trafficking defect. This was supported by the observation that incubation of these variants at lower temperature partially rescued their expression and function. Previous studies have suggested that altered SUMOylation of TRPM4 may cause a gain of function; however, we did not find any evidence that supports SUMOylation as being directly involved for the gain-of-function variant.
Conclusions: This study underpins the role of TRPM4 in the cardiac conduction system. The loss-of-function variants A432T/G582S found in 2 unrelated patients with atrioventricular block are most likely caused by misfolding-dependent altered trafficking. The ability to rescue this variant with lower temperature may provide a novel use of pharmacological chaperones in treatment strategies.
Keywords: atrioventricular block; mutations; temperature‐dependent rescue; transient receptor potential melastatin member 4.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transient receptor potential melastatin 4 cation channel in pediatric heart block.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Oct;21(4 Suppl):79-84. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29165759
-
Aberrant Deactivation-Induced Gain of Function in TRPM4 Mutant Is Associated with Human Cardiac Conduction Block.Cell Rep. 2018 Jul 17;24(3):724-731. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.034. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30021168
-
Targeted resequencing identifies TRPM4 as a major gene predisposing to progressive familial heart block type I.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Mar 15;207:349-58. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.01.052. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26820365
-
TRPM4 channels in the cardiovascular system: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 1;84(7):873-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.06.021. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22750058 Review.
-
TRPM4.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:461-87. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_18. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756717 Review.
Cited by
-
Propagation Failure by TRPM4 Overexpression.Biophys J. 2019 Feb 5;116(3):469-476. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.11.3137. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 30598284 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of TRPM4 in Cardiac Electrophysiology and Arrhythmogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 22;24(14):11798. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411798. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ion channel TRPM4 in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and in a model of glutamate-induced neuronal degeneration.Mol Brain. 2018 Jul 11;11(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0385-4. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 29996905 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a binding site for small molecule inhibitors targeting human TRPM4.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 19;16(1):833. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56131-2. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39828793 Free PMC article.
-
Four TRPM4 Cation Channel Mutations Found in Cardiac Conduction Diseases Lead to Altered Protein Stability.Front Physiol. 2018 Mar 8;9:177. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00177. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29568272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baruteau AE, Behaghel A, Fouchard S, Mabo P, Schott JJ, Dina C, Chatel S, Villain E, Thambo JB, Marcon F, Gournay V, Rouault F, Chantepie A, Guillaumont S, Godart F, Martins RP, Delasalle B, Bonnet C, Fraisse A, Schleich JM, Lusson JR, Dulac Y, Daubert JC, Le Marec H, Probst V. Parental electrocardiographic screening identifies a high degree of inheritance for congenital and childhood nonimmune isolated atrioventricular block. Circulation. 2012;126:1469–1477. - PubMed
-
- Xiao GQ, Hu K, Boutjdir M. Direct inhibition of expressed cardiac L‐ and T‐type calcium channels by IgG from mothers whose children have congenital heart block. Circulation. 2001;103:1599–1604. - PubMed
-
- Xiao GQ, Qu Y, Hu K, Boutjdir M. Down‐regulation of L‐type calcium channel in pups born to 52 kDa SSA/Ro immunized rabbits. FASEB J. 2001;15:1539–1545. - PubMed
-
- Korb D, Tng PY, Milenkovic VM, Reichhart N, Strauss O, Ritter O, Fischer T, Benz PM, Schuh K. Identification of PDZ domain containing proteins interacting with 1.2 and PMCA4b. ISRN Cell Biol. 2013;2013:16.
-
- Prall OW, Elliott DA, Harvey RP. Developmental paradigms in heart disease: insights from tinman. Ann Med. 2002;34:148–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

