Multimarker Risk Stratification in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 27207959
- PMCID: PMC4889163
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002586
Multimarker Risk Stratification in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Several biomarkers have individually been shown to be useful for risk stratification in patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI). The optimal multimarker strategy remains undefined.
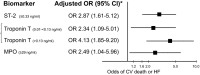
Methods and results: Biomarkers representing different pathobiological axes were studied, including myocardial stress/structural changes (NT-pro B-type natriuretic peptide [NT-proBNP], midregional proatrial natriuretic peptide [MR-proANP], suppression of tumorigenicity 2 [ST2], galectin-3, midregional proadrenomedullin [MR-proADM], and copeptin), myonecrosis (troponin T), and inflammation (myeloperoxidase [MPO], high sensitivity C-reactive protein [hsCRP], pregnancy-associated plasma protein A [PAPP-A], and growth-differentiation factor-15 [GDF-15]), in up to 1258 patients from Clopidogrel as Adjunctive Reperfusion Therapy-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 28 (CLARITY-TIMI 28), a randomized trial of clopidogrel in ST-elevation MI (STEMI). Patients were followed for 30 days. Biomarker analyses were adjusted for traditional clinical variables. Forward step-wise selection was used to assess a multimarker strategy. After adjustment for clinical variables and using a dichotomous cutpoint, 7 biomarkers were each significantly associated with a higher odds of cardiovascular death or heart failure (HF) through 30 days, including NT-proBNP (adjusted odds ratio [ORadj], 2.54; 95% CI, 1.47-4.37), MR-proANP (2.18; 1.27-3.76), ST2 (2.88; 1.72-4.81), troponin T (4.13; 1.85-9.20), MPO (2.75; 1.20-6.27), hsCRP (1.96, 1.17-3.30), and PAPP-A (3.04; 1.17-7.88). In a multimarker model, 3 biomarkers emerged as significant and complementary predictors of cardiovascular death or HF: ST2 (ORadj, 2.87; 1.61-5.12), troponin T (2.34; 1.09-5.01 and 4.13, 1.85-9.20, respectively for intermediate and high levels), and MPO (2.49; 1.04-5.96). When added to the TIMI STEMI Risk Score alone, the multimarker risk score significantly improved the C-statistic (area under the curve, 0.75 [95% CI, 0.69-0.81] to 0.82 [0.78-0.87]; P=0.001), net reclassification index (0.93; P<0.001), and integrated discrimination index (0.09; P<0.001).
Conclusions: In patients with STEMI, a multimarker strategy that combines biomarkers across pathobiological axes of myocardial stress, myocyte necrosis, and inflammation provides incremental prognostic information for prediction of cardiovascular death or HF.
Keywords: ST‐elevation myocardial infarction; Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction risk score; biomarkers; multimarker; prognosis.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


References
-
- Morrow DA, Rifai N, Antman EM, Weiner DL, McCabe CH, Cannon CP, Braunwald E. C‐reactive protein is a potent predictor of mortality independently and in combination with troponin T in acute coronary syndromes: a TIMI 11A substudy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:1460–1465. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl B, Toss H, Siegbahn A, Venge P, Wallentin L; for the FRISC Study Group . Fragmin during instability in coronary artery disease. Markers of myocardial damage and inflammation in relation to long‐term mortality in unstable coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1139–1147. - PubMed
-
- Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, Gibson CM, Murphy SA, Rifai N, McCabe C, Antman EM, Cannon CP, Braunwald E. Multimarker approach to risk stratification in non‐ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: simultaneous assessment of troponin I, C‐reactive protein, and B‐type natriuretic peptide. Circulation. 2002;105:1760–1763. - PubMed
-
- James SK, Lindahl B, Siegbahn A, Stridsberg M, Venge P, Armstrong P, Barnathan ES, Califf R, Topol EJ, Simoons ML, Wallentin L. N‐terminal pro‐brain natriuretic peptide and other risk markers for the separate prediction of mortality and subsequent myocardial infarction in patients with unstable coronary artery disease: a Global Utilization of Strategies To Open occluded arteries (GUSTO)‐IV substudy. Circulation. 2003;108:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Tello‐Montoliu A, Marin F, Roldan V, Mainar L, Lopez MT, Sogorb F, Vicente V, Lip GY. A multimarker risk stratification approach to non‐ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: implications of troponin T, CRP, NT pro‐BNP and fibrin D‐dimer levels. J Intern Med. 2007;262:651–658. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

