3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126) Decreases Hepatic and Systemic Ratios of Epoxide to Diol Metabolites of Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Male Rats
- PMID: 27208083
- PMCID: PMC4960907
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw084
3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126) Decreases Hepatic and Systemic Ratios of Epoxide to Diol Metabolites of Unsaturated Fatty Acids in Male Rats
Abstract
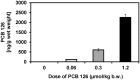
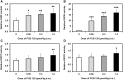
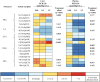
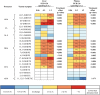
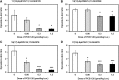
Disruption of the homeostasis of oxygenated regulatory lipid mediators (oxylipins), potential markers of exposure to aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonists, such as 3,3',4,4',5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126), is associated with a range of diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Here we test the hypothesis that PCB 126 exposure alters the levels of oxylipins in rats. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (5-weeks old) were treated over a 3-month period every 2 weeks with intraperitoneal injections of PCB 126 in corn oil (cumulative doses of 0, 19.8, 97.8, and 390 µg/kg b.w.; 6 injections total). PCB 126 treatment caused a reduction in growth rates at the highest dose investigated, a dose-dependent decrease in thymus weights, and a dose-dependent increase in liver weights. Liver PCB 126 levels increased in a dose-dependent manner, while levels in plasma were below or close to the detection limit. The ratios of several epoxides to diol metabolites formed via the cytochrome P450 (P450) monooxygenase/soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) pathway from polyunsaturated fatty acids displayed a dose-dependent decrease in the liver and plasma, whereas levels of oxylipins formed by other metabolic pathways were generally not altered by PCB 126 treatment. The effects of PCB 126 on epoxide-to-diol ratios were associated with an increased CYP1A activity in liver microsomes and an increased sEH activity in liver cytosol and peroxisomes. These results suggest that oxylipins are potential biomarkers of exposure to PCB 126 and that the P450/sEH pathway is a therapeutic target for PCB 126-mediated hepatotoxicity that warrants further attention.
Keywords: CYP1A; oxylipin; persistent organic pollutants; polychlorinated biphenyls; soluble epoxide hydrolase.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology. All rights reserved. for Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Aboutabl M. E., Zordoky B. N., Hammock B. D., El-Kadi A. O. (2011). Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase confers cardioprotection and prevents cardiac cytochrome P450 induction by benzo(a)pyrene. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 57, 273–281. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Lloret P., Lind P. M., Nyberg I., Orberg J., Rodríguez-Navarro A. B. (2009). Effects of 3,3',4,4',5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126) on vertebral bone mineralization and on thyroxin and vitamin D levels in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol. Lett. 187, 63–68. - PubMed
-
- Amara I. E., Elshenawy O. H., Abdelrady M., El-Kadi A. O. (2014). Acute mercury toxicity modulates cytochrome P450, soluble epoxide hydrolase and their associated arachidonic acid metabolites in C57Bl/6 mouse heart. Toxicol. Lett. 226, 53–62. - PubMed
-
- Bandiera S., Safe S., Okey A. B. (1982). Binding of polychlorinated biphenyls classified as either phenobarbitone, 3-methylcholanthrene or mixed-type inducers to cytosolic Ah receptor. Chem. Biol. Interact. 39, 259–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

