Alternative Splicing of Rice WRKY62 and WRKY76 Transcription Factor Genes in Pathogen Defense
- PMID: 27208272
- PMCID: PMC4902586
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.01921
Alternative Splicing of Rice WRKY62 and WRKY76 Transcription Factor Genes in Pathogen Defense
Abstract
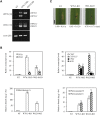
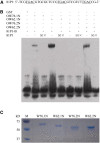
The WRKY family of transcription factors (TFs) functions as transcriptional activators or repressors in various signaling pathways. In this study, we discovered that OsWRKY62 and OsWRKY76, two genes of the WRKY IIa subfamily, undergo constitutive and inducible alternative splicing. The full-length OsWRKY62.1 and OsWRKY76.1 proteins formed homocomplexes and heterocomplexes, and the heterocomplex dominates in the nuclei when analyzed in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. Transgenic overexpression of OsWRKY62.1 and OsWRKY76.1 in rice (Oryza sativa) enhanced plant susceptibility to the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae and the leaf blight bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae, whereas RNA interference and loss-of-function knockout plants exhibited elevated resistance. The dsOW62/76 and knockout lines of OsWRKY62 and OsWRKY76 also showed greatly increased expression of defense-related genes and the accumulation of phytoalexins. The ratio of full-length versus truncated transcripts changed in dsOW62/76 plants as well as in response to pathogen infection. The short alternative OsWRKY62.2 and OsWRKY76.2 isoforms could interact with each other and with full-length proteins. OsWRKY62.2 showed a reduced repressor activity in planta, and two sequence determinants required for the repressor activity were identified in the amino terminus of OsWRKY62.1. The amino termini of OsWRKY62 and OsWRKY76 splice variants also showed reduced binding to the canonical W box motif. These results not only enhance our understanding of the DNA-binding property, the repressor sequence motifs, and the negative feedback regulation of the IIa subfamily of WRKYs but also provide evidence for alternative splicing of WRKY TFs during the plant defense response.
© 2016 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures


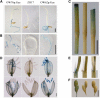
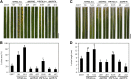
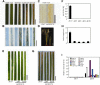
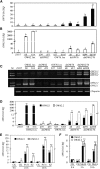


References
-
- Agarwal P, Reddy MP, Chikara J (2011) WRKY: its structure, evolutionary relationship, DNA-binding selectivity, role in stress tolerance and development of plants. Mol Biol Rep 38: 3883–3896 - PubMed
-
- Chujo T, Kato T, Yamada K, Takai R, Akimoto-Tomiyama C, Minami E, Nagamura Y, Shibuya N, Yasuda M, Nakashita H, et al. (2008) Characterization of an elicitor-induced rice WRKY gene, OsWRKY71. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72: 240–245 - PubMed
-
- Chujo T, Miyamoto K, Shimogawa T, Shimizu T, Otake Y, Yokotani N, Nishizawa Y, Shibuya N, Nojiri H, Yamane H, et al. (2013) OsWRKY28, a PAMP-responsive transrepressor, negatively regulates innate immune responses in rice against rice blast fungus. Plant Mol Biol 82: 23–37 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

