Hierarchical glucocorticoid-endocannabinoid interplay regulates the activation of the nucleus accumbens by insulin
- PMID: 27208730
- PMCID: PMC8041101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.05.009
Hierarchical glucocorticoid-endocannabinoid interplay regulates the activation of the nucleus accumbens by insulin
Abstract
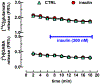
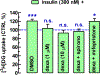
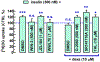
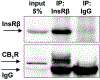
Here we asked if insulin activation of the nucleus accumbens in vitro is reflected by an increase in (3)H-deoxyglucose ([(3)H]DG) uptake, thus subserving a new model to study molecular mechanisms of central insulin actions. Additionally, we investigated the dependence of this insulin effect on endocannabinoids and corticosteroids, two major culprits in insulin resistance. We found that in acute accumbal slices, insulin (3 and 300nM but not at 0.3nM) produced an increase in [(3)H]DG uptake. The synthetic cannabinoid agonist, WIN55212-2 (500nM) and the glucocorticoid dexamethasone (10μM), impaired insulin (300nM) action on [(3)H]DG uptake. The glucocorticoid receptor (GcR) antagonist, mifepristone (10μM) prevented dexamethasone from inhibiting insulin's action. Strikingly, this anti-insulin action of dexamethasone was also blocked by two CB1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1R) antagonists, O-2050 (500nM) and SR141716A (500nM), as well as by tetrahydrolipstatin (10μM), an inhibitor of diacylglycerol lipases-the enzymes responsible for the synthesis of the endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol (2-AG). On the other hand, the blockade of the post-synaptic 2-AG metabolizing enzymes, α,β-serine hydrolase domain 6/12 by WWL70 (1μM) also prevented the action of insulin, probably via increasing endogenous 2-AG tone. Additionally, an anti-insulin receptor (InsR) antibody immunoprecipitated CB1Rs from accumbal homogenates, indicating a physical complexing of CB1Rs with InsRs that supports their functional interaction. Altogether, insulin stimulates glucose uptake in the nucleus accumbens. Accumbal GcR activation triggers the synthesis of 2-AG that in turn binds to the known CB1R-InsR heteromer, thus impeding insulin signaling.
Keywords: 2-Arachidonoylglycerol; CB(1)R cannabinoid receptor; Glucocorticoid receptor; Glucose uptake; Insulin; Nucleus accumbens.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute Stress Suppresses Synaptic Inhibition and Increases Anxiety via Endocannabinoid Release in the Basolateral Amygdala.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 10;36(32):8461-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2279-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27511017 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of presynaptic interaction between glucocorticoid and CB1 cannabinoid receptors in GABA- and glutamatergic terminals in the frontal cortex of laboratory rodents.Neurochem Int. 2015 Nov;90:72-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Jul 18. Neurochem Int. 2015. PMID: 26196379
-
Suppression of outward K⁺ currents by WIN55212-2 in rat retinal ganglion cells is independent of CB1/CB2 receptors.Neuroscience. 2013 Dec 3;253:183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.056. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 24013008
-
Modulation of electrically evoked acetylcholine release through cannabinoid CB1 receptors: evidence for an endocannabinoid tone in the human neocortex.Neuroscience. 2003;120(2):455-65. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00318-x. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12890515
-
Angiotensin II induces vascular endocannabinoid release, which attenuates its vasoconstrictor effect via CB1 cannabinoid receptors.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 7;287(37):31540-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.346296. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22787147 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anandamide Effects in a Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer's Disease-Like Sporadic Dementia in Rats.Front Neurosci. 2018 Sep 21;12:653. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00653. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30333717 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic insulinopenia/hyperglycemia decreases cannabinoid CB1 receptor density and impairs glucose uptake in the mouse forebrain.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Apr;147:101-109. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.01.024. Epub 2019 Feb 2. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30721768 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cannabinoid receptor 1 in human adipose tissue for lipolysis regulation and insulin resistance.Endocrine. 2017 Mar;55(3):839-852. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-1172-6. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 27858284 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed Membrane Signaling by Glucocorticoids.Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2022 Oct;26:100390. doi: 10.1016/j.coemr.2022.100390. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2022. PMID: 38075196 Free PMC article.
-
Transient gain of function of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the control of frontocortical glucose consumption in a rat model of Type-1 diabetes.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Aug;161:106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 May 16. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32428627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anthony K, Reed LJ, Dunn JT, Bingham E, Hopkins D, Marsden PK, Amiel SA, 2006. Attenuation of insulin-evoked responses in brain networks controlling appetite and reward in insulin resistance: the cerebral basis for impaired control of food intake in metabolic syndrome? Diabetes 55, 2986–2992. doi:10.2337/db06-0376 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baptista FI, Gaspar JM, Cristóvão A, Santos PF, Köfalvi A, Ambrósio AF, 2011. Diabetes induces early transient changes in the content of vesicular transporters and no major effects in neurotransmitter release in hippocampus and retina. Brain Res. 1383, 257–269. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.071 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

