A systematic, large-scale comparison of transcription factor binding site models
- PMID: 27209209
- PMCID: PMC4875604
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2729-8
A systematic, large-scale comparison of transcription factor binding site models
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: A systematic, large-scale comparison of transcription factor binding site models.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jul 20;17(1):502. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2818-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27440159 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
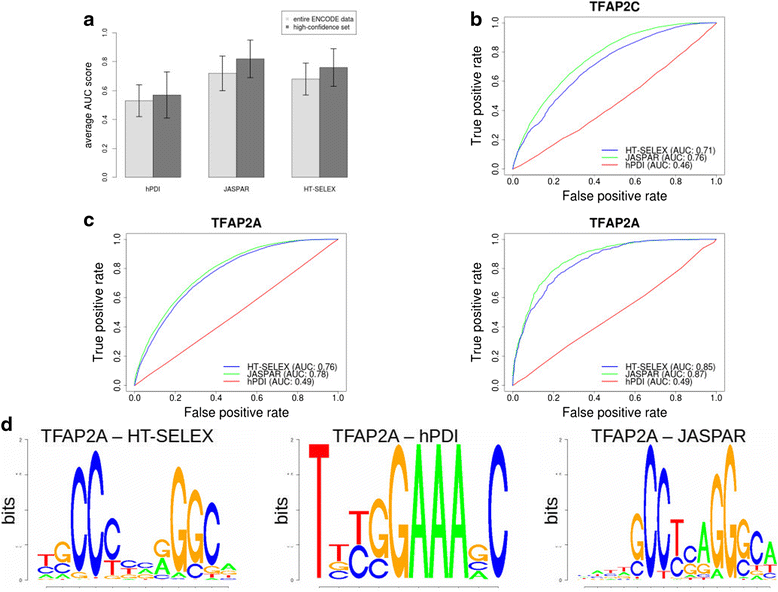
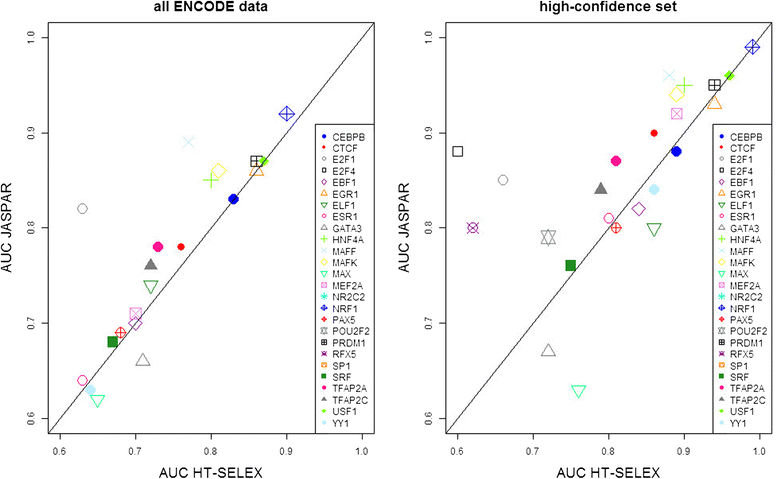
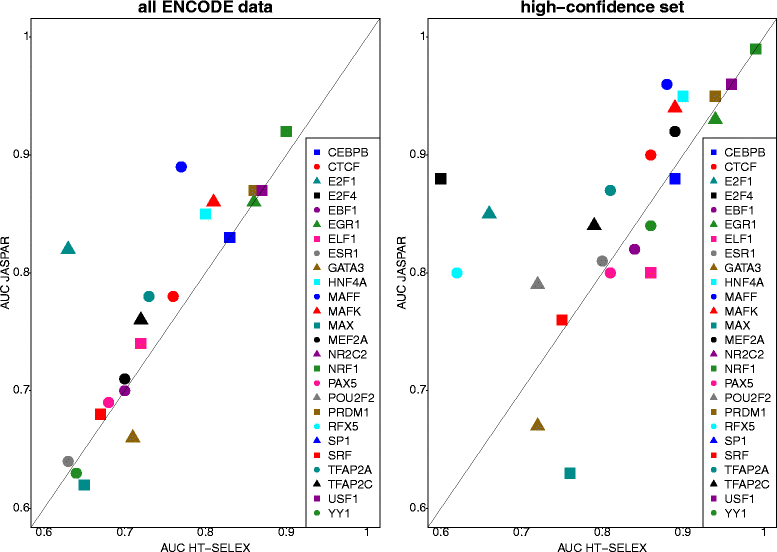
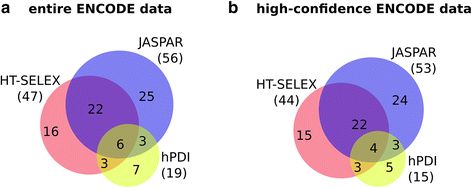
Background: The modelling of gene regulation is a major challenge in biomedical research. This process is dominated by transcription factors (TFs) and mutations in their binding sites (TFBSs) may cause the misregulation of genes, eventually leading to disease. The consequences of DNA variants on TF binding are modelled in silico using binding matrices, but it remains unclear whether these are capable of accurately representing in vivo binding. In this study, we present a systematic comparison of binding models for 82 human TFs from three freely available sources: JASPAR matrices, HT-SELEX-generated models and matrices derived from protein binding microarrays (PBMs). We determined their ability to detect experimentally verified "real" in vivo TFBSs derived from ENCODE ChIP-seq data. As negative controls we chose random downstream exonic sequences, which are unlikely to harbour TFBS. All models were assessed by receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis.
Results: While the area-under-curve was low for most of the tested models with only 47 % reaching a score of 0.7 or higher, we noticed strong differences between the various position-specific scoring matrices with JASPAR and HT-SELEX models showing higher success rates than PBM-derived models. In addition, we found that while TFBS sequences showed a higher degree of conservation than randomly chosen sequences, there was a high variability between individual TFBSs.
Conclusions: Our results show that only few of the matrix-based models used to predict potential TFBS are able to reliably detect experimentally confirmed TFBS. We compiled our findings in a freely accessible web application called ePOSSUM ( http:/mutationtaster.charite.de/ePOSSUM/ ) which uses a Bayes classifier to assess the impact of genetic alterations on TF binding in user-defined sequences. Additionally, ePOSSUM provides information on the reliability of the prediction using our test set of experimentally confirmed binding sites.
Keywords: Genetic variation; PSSM; TFBS prediction; Transcription factor binding sites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription Factor Information System (TFIS): A Tool for Detection of Transcription Factor Binding Sites.Interdiscip Sci. 2017 Sep;9(3):378-391. doi: 10.1007/s12539-016-0168-5. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Interdiscip Sci. 2017. PMID: 27052996
-
EMQIT: a machine learning approach for energy based PWM matrix quality improvement.Biol Direct. 2017 Aug 1;12(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13062-017-0189-y. Biol Direct. 2017. PMID: 28764727 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and structural considerations of TF-DNA binding for the generation of biologically meaningful and accurate phylogenetic footprinting analysis: the LysR-type transcriptional regulator family as a study model.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 27;17(1):686. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3025-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27567672 Free PMC article.
-
Building Transcription Factor Binding Site Models to Understand Gene Regulation in Plants.Mol Plant. 2019 Jun 3;12(6):743-763. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Mol Plant. 2019. PMID: 30447332 Review.
-
[Advances on bioinformatic research in transcription factor binding sites].Yi Chuan. 2009 Apr;31(4):365-73. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2009.00365. Yi Chuan. 2009. PMID: 19586888 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Insight on Transcriptional Regulation of the Energy Sensing AMPK and Biosynthetic mTOR Pathway Genes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 29;8:671. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00671. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32903688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technologies for profiling the impact of genomic variants on transcription factor binding.Med Genet. 2021 Aug 14;33(2):147-155. doi: 10.1515/medgen-2021-2073. eCollection 2021 Jun. Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 38836027 Free PMC article.
-
Common TDP1 Polymorphisms in Relation to Survival among Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Multicenter Study from the International Lung Cancer Consortium.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 15;23(24):7550-7557. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1401. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28974547 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological functions of transcriptional enhancers.Nat Neurosci. 2020 Jan;23(1):5-14. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0538-5. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Nat Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31740812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTBP2 - a gene with relevance for both Anorexia nervosa and body weight regulation.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Jun 9;12(1):241. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02018-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35680849 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

