Alteration of matrix metalloproteinase-3 O-glycan structure as a biomarker for disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 27209430
- PMCID: PMC4875599
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1013-2
Alteration of matrix metalloproteinase-3 O-glycan structure as a biomarker for disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Nearly all secreted proteins are glycosylated, and serum glycoproteins that exhibit disease-associated glycosylation changes have potential to be biomarkers. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), C-reactive protein (CRP), and matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) are widely used as serologic biomarkers, but they lack sufficient specificity or precision. We performed comparative glycosylation profiling of MMP-3 using a recently developed antibody-overlay lectin microarray technology that allows semicomprehensive and quantitative analysis of specific protein glycosylation to develop an RA-specific disease activity biomarker.
Methods: Serum was taken from patients with RA (n = 24) whose disease activity was scored using composite measures, and MMP-3 was immunoprecipitated and subjected to lectin microarray analysis. A disease activity index (DAI) based on lectin signal was developed and validated using another cohort (n = 60). Synovial fluid MMP-3 in patients with RA and patients with osteoarthritis (OA) was also analyzed.
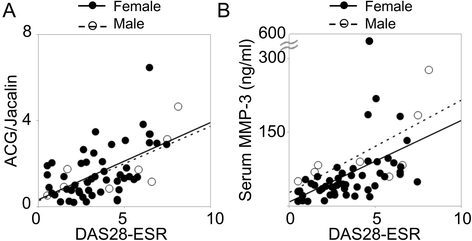
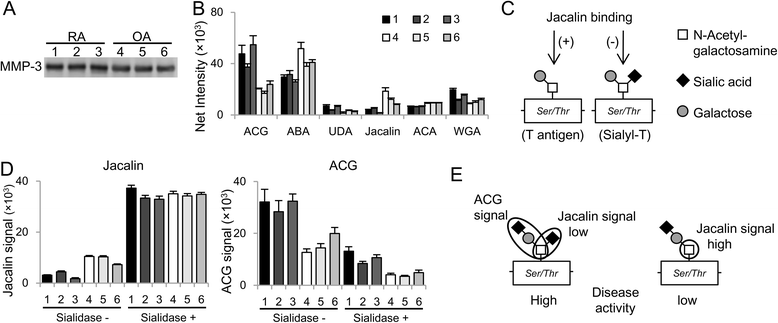
Results: Intense signals were observed on a sialic acid-binding lectin (Agrocybe cylindracea galectin [ACG]) and O-glycan-binding lectins (Jacalin, Agaricus bisporus agglutinin [ABA], and Amaranthus caudatus agglutinin [ACA]) by applying subnanogram levels of serum MMP-3. ACG, ABA, and ACA revealed differences in MMP-3 quantity, and Jacalin revealed differences in MMP-3 quality. The resultant index, ACG/Jacalin, correlated well with disease activity. Further validation using another cohort confirmed that this index correlated well with several DAIs and their components, and reflected DAI changes following RA treatment, with correlations greater than those for MMP-3 and CRP. Furthermore, MMP-3, which generated a high ACG/Jacalin score, accumulated in synovial fluid of patients with RA but not in that of patients with OA. Sialidase digestion revealed that the difference in quality was derived from O-glycan α-2,6-sialylation.
Conclusions: This is the first report of a glycoprotein biomarker using glycan change at a local lesion to assess disease activity in autoimmune diseases. Differences in the degree of serum MMP-3 α-2,6-sialylation may be a useful index for estimating disease activity.
Keywords: Biomarker; Glycoprotein; MMP-3; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinases MMP-3 and MMP-1 levels in sera and synovial fluids in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.Ital J Biochem. 2005 Sep-Dec;54(3-4):248-57. Ital J Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16688934
-
[Levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator in knee synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis].Ryumachi. 1997 Feb;37(1):3-8. Ryumachi. 1997. PMID: 9128417 Japanese.
-
Circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-3 and MMP-1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1), and MMP-1/TIMP-1 complex in rheumatic disease. Correlation with clinical activity of rheumatoid arthritis versus other surrogate markers.J Rheumatol. 1999 Feb;26(2):251-8. J Rheumatol. 1999. PMID: 9972954
-
Evaluating the potential of matrix metalloproteinase as a diagnostic biomarker in rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13;102(41):e35340. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035340. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37832126 Free PMC article.
-
MMP3 is a reliable marker for disease activity, radiological monitoring, disease outcome predictability, and therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Aug;32(4):550-562. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2019.01.006. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 31174824 Review.
Cited by
-
A standardized method for lectin microarray-based tissue glycome mapping.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 6;7:43560. doi: 10.1038/srep43560. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28262709 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and global protein glycosylation are differentially expressed in healthy and osteoarthritic equine carpal synovial fluid.Equine Vet J. 2022 Mar;54(2):323-333. doi: 10.1111/evj.13440. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Equine Vet J. 2022. PMID: 33587757 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in disialyl-T antigen levels in mice deficient for both St6galnac3 and St6galnac4 results in blood filling of lymph nodes.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 29;13(1):10582. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37363-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37386100 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering disease through glycan codes: leveraging lectin microarrays for clinical insights.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Aug 1;56(8):1145-1155. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024123. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39099413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Lectin Microarrays for Biomarker Discovery.ChemistryOpen. 2020 Mar 2;9(3):285-300. doi: 10.1002/open.201900326. eCollection 2020 Mar. ChemistryOpen. 2020. PMID: 32154049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Prevoo ML, van ’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts: development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:44–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380107. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

