Hepatitis B virus inhibits intrinsic RIG-I and RIG-G immune signaling via inducing miR146a
- PMID: 27210312
- PMCID: PMC4876503
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26150
Hepatitis B virus inhibits intrinsic RIG-I and RIG-G immune signaling via inducing miR146a
Abstract
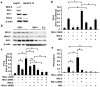
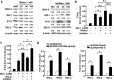
Previous studies showed that hepatitis B virus (HBV), as a latency invader, attenuated host anti-viral immune responses. miRNAs were shown to be involved in HBV infection and HBV-related diseases, however, the precise role of miRNAs in HBV-mediated immunosuppression remains unclear. Here, we observed that down-regulated RIG-I like receptors might be one critical mechanism of HBV-induced suppression of type I IFN transcription in both HBV(+) hepatoma cell lines and liver cancer tissues. Then, miR146a was demonstrated to negatively regulate the expression of RIG-I-like receptors by directly targeting both RIG-I and RIG-G. Further investigation showed that antagonizing miR146a by anti-sense inhibitors or sponge approach accelerated HBV clearance and reduced HBV load both in vitro and in a HBV-carrying mouse model. Therefore, our findings indicated that HBV-induced miR146a attenuates cell-intrinsic anti-viral innate immunity through targeting RIG-I and RIG-G, and silencing miR146a might be an effective target to reverse HBV-induced immune suppression.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 senses hepatitis B virus and activates innate immune signaling to suppress virus replication.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 15;191(6):3264-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300512. Epub 2013 Aug 7. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23926323
-
miR146a impairs the IFN-induced anti-HBV immune response by downregulating STAT1 in hepatocytes.Liver Int. 2014 Jan;34(1):58-68. doi: 10.1111/liv.12244. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 23890093
-
5'-triphosphate-siRNA activates RIG-I-dependent type I interferon production and enhances inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in HepG2.2.15 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):86-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.050. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24099962
-
The Interactions between HBV and the Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes.Viruses. 2020 Mar 5;12(3):285. doi: 10.3390/v12030285. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32151000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The mechanism of HBV disruption on RIG-I signaling pathway].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Oct;29(5):995-8, 1013. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23198448 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
A MicroRNA-Based Method for High-Viremia Detection-A New Approach on a Romanian Lot of Chronically Infected Patients with Hepatitis B Virus.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;13(22):3425. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223425. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998561 Free PMC article.
-
Viral evasion of the interferon response at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2023 Jun 15;136(12):jcs260682. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260682. Epub 2023 Jun 21. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37341132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in the Regulation of RIG-I-like Receptor Signaling Pathway: Possible Strategy for Viral Infection and Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 4;13(9):1344. doi: 10.3390/biom13091344. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MITA/STING and Its Alternative Splicing Isoform MRP Restrict Hepatitis B Virus Replication.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 5;12(1):e0169701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169701. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28056087 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic Acid-Induced Signaling in Chronic Viral Liver Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 5;11:624034. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.624034. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33613561 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

