Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
- PMID: 27210421
- PMCID: PMC4876372
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26521
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
Abstract
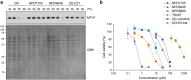
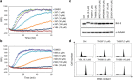
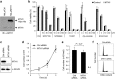
Since recent publications suggested that the survival of cancer cells depends on MTH1 to avoid incorporation of oxidized nucleotides into the cellular DNA, MTH1 has attracted attention as a potential cancer therapeutic target. In this study, we identified new purine-based MTH1 inhibitors by chemical array screening. However, although the MTH1 inhibitors identified in this study targeted cellular MTH1, they exhibited only weak cytotoxicity against cancer cells compared to recently reported first-in-class inhibitors. We performed proteomic profiling to investigate the modes of action by which chemically distinct MTH1 inhibitors induce cancer cell death, and found mechanistic differences among the first-in-class MTH1 inhibitors. In particular, we identified tubulin as the primary target of TH287 and TH588 responsible for the antitumor effects despite the nanomolar MTH1-inhibitory activity in vitro. Furthermore, overexpression of MTH1 did not rescue cells from MTH1 inhibitor-induced cell death, and siRNA-mediated knockdown of MTH1 did not suppress cancer cell growth. Taken together, we conclude that the cytotoxicity of MTH1 inhibitors is attributable to off-target effects and that MTH1 is not essential for cancer cell survival.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Validation and development of MTH1 inhibitors for treatment of cancer.Ann Oncol. 2016 Dec;27(12):2275-2283. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw429. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27827301
-
MTH1 inhibition eradicates cancer by preventing sanitation of the dNTP pool.Nature. 2014 Apr 10;508(7495):215-21. doi: 10.1038/nature13181. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24695224
-
MTH1 deficiency selectively increases non-cytotoxic oxidative DNA damage in lung cancer cells: more bad news than good?BMC Cancer. 2018 Apr 16;18(1):423. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4332-7. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29661172 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MTH1 in oxidative stress and therapeutic targeting of cancer.Redox Biol. 2024 Nov;77:103394. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103394. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39418911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Significance of NUDT1 (MTH1) Across Cancer Types.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 27;26(11):5137. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115137. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A patient-derived xenograft pre-clinical trial reveals treatment responses and a resistance mechanism to karonudib in metastatic melanoma.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jul 24;9(8):810. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0865-6. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30042422 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 upregulates the cellular antioxidant defense to enable B-cell growth transformation and immortalization.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(3):603-616. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1003-3. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31511648 Free PMC article.
-
Potent and specific MTH1 inhibitors targeting gastric cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jun 4;10(6):434. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1665-3. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31164636 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled 6-(2, 3-Dichlorophenyl)-N4-methylpyrimidine-2, 4-diamine (TH287): A Potential Radiotracer for Measuring and Imaging MTH1.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 23;21(22):8860. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228860. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33238630 Free PMC article.
-
AXL and CAV-1 play a role for MTH1 inhibitor TH1579 sensitivity in cutaneous malignant melanoma.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Jul;27(7):2081-2098. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0488-1. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31919461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trachootham D., Alexandre J. & Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 579–591 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Hu Y. et al. Mitochondrial manganese-superoxide dismutase expression in ovarian cancer: role in cell proliferation and response to oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 39485–39492 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Xia C. et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate angiogenesis and tumor growth through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 67, 10823–10830 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

