Overcoming resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in solid tumor cells by simultaneously targeting death receptors, c-FLIP and IAPs
- PMID: 27210546
- PMCID: PMC4902065
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3525
Overcoming resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in solid tumor cells by simultaneously targeting death receptors, c-FLIP and IAPs
Abstract
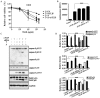
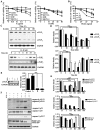
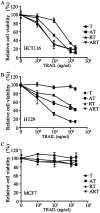
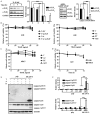
The discovery of the TRAIL protein and its death receptors DR4/5 changed the horizon of cancer research because TRAIL specifically kills cancer cells. However, the validity of TRAIL-based cancer therapies has yet to be established, as most cancer cells are TRAIL-resistant. In this report, we demonstrate that TRAIL-resistance of many cancer cell lines can be overcome after siRNA- or rocaglamide-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP expression and simultaneous inhibition of IAPs activity using AT406, a pan-antagonist of IAPs. Combined triple actions of the TRAIL, the IAPs inhibitor, AT406, and the c-FLIP expression inhibitor, rocaglamide (ART), markedly improve TRAIL-induced apoptotic effects in most solid cancer cell lines through the activation of an extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Furthermore, this ART combination does not harm normal cells. Among the 18 TRAIL-resistant cancer cell lines used, 15 cell lines become sensitive or highly sensitive to ART, and two out of three glioma cell lines exhibit high resistance to ART treatment due to very low levels of procaspase-8. This study provides a rationale for the development of TRAIL-induced apoptosis-based cancer therapies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of c-FLIP by RNAi enhances sensitivity of the human osteogenic sarcoma cell line U2OS to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(6):2251-6. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.6.2251. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25824746
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
-
Inhibition of BET bromodomain-dependent XIAP and FLIP expression sensitizes KRAS-mutated NSCLC to pro-apoptotic agents.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Sep 8;7(9):e2365. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.271. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27607580 Free PMC article.
-
The XIAP inhibitor Embelin enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in malignant glioma cells by down-regulation of the short isoform of FLIP.Neurochem Int. 2009 Nov;55(6):423-30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2009.04.011. Epub 2009 May 4. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19409438
-
Overcoming chemotherapy drug resistance by targeting inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs).Apoptosis. 2017 Jul;22(7):898-919. doi: 10.1007/s10495-017-1375-1. Apoptosis. 2017. PMID: 28424988 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Naphthyridine Derivative, 3u, Induces Necroptosis at Low Concentrations and Apoptosis at High Concentrations in Human Melanoma A375 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 29;19(10):2975. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102975. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30274263 Free PMC article.
-
Should We Keep Walking along the Trail for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment? Revisiting TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand for Anticancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 18;10(3):77. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030077. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29562636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cell line modified to express a potent, DR5 specific variant of TRAIL, show enhanced cytotoxicity in ovarian cancer models.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 19;10(15):e34976. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34976. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170449 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal delivery of TRAIL and miR‑335 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Jan;51(1):3. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5206. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36416311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Curcumin Analogues DMC and EF24 in Combination with the Cytokine TRAIL against Kidney Cancer.Molecules. 2021 Oct 18;26(20):6302. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206302. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684883 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

