Creation of a Large Adipose Tissue Construct in Humans Using a Tissue-engineering Chamber: A Step Forward in the Clinical Application of Soft Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 27211566
- PMCID: PMC4856786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.03.032
Creation of a Large Adipose Tissue Construct in Humans Using a Tissue-engineering Chamber: A Step Forward in the Clinical Application of Soft Tissue Engineering
Abstract
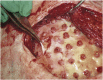
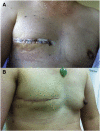
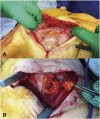
Tissue engineering is currently exploring new and exciting avenues for the repair of soft tissue and organ defects. Adipose tissue engineering using the tissue engineering chamber (TEC) model has yielded promising results in animals; however, to date, there have been no reports on the use of this device in humans. Five female post mastectomy patients ranging from 35 to 49years old were recruited and a pedicled thoracodorsal artery perforator fat flap ranging from 6 to 50ml was harvested, transposed onto the chest wall and covered by an acrylic perforated dome-shaped chamber ranging from 140 to 350cm(3). Magnetic resonance evaluation was performed at three and six months after chamber implantation. Chambers were removed at six months and samples were obtained for histological analysis. In one patient, newly formed tissue to a volume of 210ml was generated inside the chamber. One patient was unable to complete the trial and the other three failed to develop significant enlargement of the original fat flap, which, at the time of chamber explantation, was encased in a thick fibrous capsule. Our study provides evidence that generation of large well-vascularized tissue engineered constructs using the TEC is feasible in humans.
Keywords: Adipose; Adipose-derived stem cells; Chamber; Inflammation; Soft tissue reconstruction; Tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Tissue Engineering Chambers: Potential Clinical Uses and Limitations.EBioMedicine. 2016 Apr;6:22-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Mar 12. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27211541 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Quo Vadis Breast Tissue Engineering?EBioMedicine. 2016 Apr;6:24-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.03.044. Epub 2016 Mar 31. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27211542 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Long-term stability of adipose tissue generated from a vascularized pedicled fat flap inside a chamber.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011 Jun;127(6):2283-2292. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182131c3e. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011. PMID: 21617462
-
Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Delivery for Adipose Tissue Engineering: Current Status and Potential Applications in a Tissue Engineering Chamber Model.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016 Aug;12(4):484-91. doi: 10.1007/s12015-016-9653-9. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016. PMID: 27075632 Review.
-
Engineering vascularized soft tissue flaps in an animal model using human adipose-derived stem cells and VEGF+PLGA/PEG microspheres on a collagen-chitosan scaffold with a flow-through vascular pedicle.Biomaterials. 2015 Dec;73:198-213. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.09.024. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26410787 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous large volume adipose tissue generation from a vascularized pedicled fat flap inside a chamber space.Tissue Eng. 2007 Apr;13(4):673-81. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0212. Tissue Eng. 2007. PMID: 17335401
-
Activated macrophages as key mediators of capsule formation on adipose constructs in tissue engineering chamber models.Cell Biol Int. 2017 Apr;41(4):354-360. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10731. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Cell Biol Int. 2017. PMID: 28102640 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue engineering and surgery: from translational studies to human trials.Innov Surg Sci. 2017 Jun 24;2(4):189-202. doi: 10.1515/iss-2017-0011. eCollection 2017 Dec. Innov Surg Sci. 2017. PMID: 31579752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large adipose tissue generation in a mussel-inspired bioreactor of elastic-mimetic cryogel and platelets.J Tissue Eng. 2018 Nov 14;9:2041731418808633. doi: 10.1177/2041731418808633. eCollection 2018 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2018. PMID: 30505425 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of scaffold-guided bone regeneration principles and microvascular tissue transfer surgery.Sci Adv. 2023 May 5;9(18):eadd6071. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add6071. Epub 2023 May 5. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37146134 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Hydrogels in Breast Cancer Therapy.Gels. 2024 Jul 19;10(7):479. doi: 10.3390/gels10070479. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39057502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining Vascularization Strategies in Tissue Engineering: The Faster Road to Success?Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Dec 8;8:592095. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.592095. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33364230 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Atala A., Bauer S.B., Soker S., Yoo J.J., Retik A.B. Tissue-engineered autologous bladders for patients needing cystoplasty. Lancet. 2006;367:1241–1246. - PubMed
-
- Birchall M.A., Seifalian A.M. Tissue engineering's green shoots of disruptive innovation. Lancet. 2014;384:288–290. - PubMed
-
- Brorson H. Adipose tissue in lymphedema: the ignorance of adipose tissue in lymphedema. Lymphology. 2004;37:175–177. - PubMed
-
- Croll T.I., O'Connor A.J., Stevens G.W., Cooper-White J.J. A blank slate? Layer-by-layer deposition of hyaluronic acid and chitosan onto various surfaces. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:1610–1622. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

