SUMO5, a Novel Poly-SUMO Isoform, Regulates PML Nuclear Bodies
- PMID: 27211601
- PMCID: PMC4876461
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26509
SUMO5, a Novel Poly-SUMO Isoform, Regulates PML Nuclear Bodies
Abstract
Promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies (PML-NBs) are PML-based nuclear structures that regulate various cellular processes. SUMOylation, the process of covalently conjugating small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMOs), is required for both the formation and the disruption of PML-NBs. However, detailed mechanisms of how SUMOylation regulates these processes remain unknown. Here we report that SUMO5, a novel SUMO variant, mediates the growth and disruption of PML-NBs. PolySUMO5 conjugation of PML at lysine 160 facilitates recruitment of PML-NB components, which enlarges PML-NBs. SUMO5 also increases polySUMO2/3 conjugation of PML, resulting in RNF4-mediated disruption of PML-NBs. The acute promyelocytic leukemia oncoprotein PML-RARα blocks SUMO5 conjugation of PML, causing cytoplasmic displacement of PML and disruption of PML-NBs. Our work not only identifies a new member of the SUMO family but also reveals the mechanistic basis of the PML-NB life cycle in human cells.
Figures
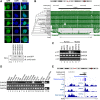
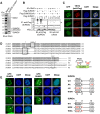
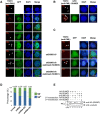
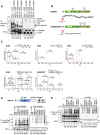
References
-
- D’Orazi G. et al. Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 phosphorylates p53 at Ser 46 and mediates apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 4, 11–19 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Szostecki C., Guldner H. H., Netter H. J. & Will H. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding a human nuclear antigen predominantly recognized by autoantibodies from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol 145, 4338–4347 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Skinner P. J. et al. Ataxin-1 with an expanded glutamine tract alters nuclear matrix-associated structures. Nature 389, 971–974 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

