Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine in caudal analgesia in children
- PMID: 27212752
- PMCID: PMC4864692
- DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.174468
Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine in caudal analgesia in children
Abstract
Context: Postoperative pain management is becoming an integral part of anesthesia care. Various techniques of pediatric pain relief have been designed among which the most commonly practiced is caudal epidural block. Several adjuvants have been used to prolong the duration of caudal analgesia such as clonidine, neostigmine, ketamine, opioids, and ephedrine. We have designed the study using dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to assess analgesic efficacy, duration of postoperative analgesia, hemodynamic stability, postoperative sedation, and any adverse effects in children.
Aims: The aim is to study the effects of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine in caudal analgesia in pediatric patients posted for infraumbilical surgeries.
Settings and design: This is a randomized, double-blind study in which effect of dexmedetomidine is studied when added to bupivacaine in the caudal epidural block. The observations are made intraoperatively for hemodynamic stability and postoperatively for the duration of analgesia.
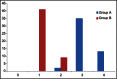
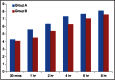
Subjects and methods: This study was conducted in 100 children of American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I and II, aged 2-10 years, undergoing elective infraumbilical surgeries. They were divided into two groups as follows: Group A: (0.25%) bupivacaine 1 ml/kg + normal saline (NS) 1 ml. Group B: (0.25%) bupivacaine 1 ml/kg + 1 μg/kg dexmedetomidine in 1 ml NS. As this study was double-blind, patients were randomly assigned to receive either (bupivacaine + saline) or (bupivacaine + dexmedetomidine) in each group. The patients were observed for hemodynamic stability, respiratory depression, and postoperative pain using face, legs, activity, cry, consolability (FLACC) pain scale for 24 h postoperatively.
Statistical analysis used: Unpaired Student's t-test.
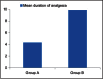
Results: The mean duration of effective analgesia in Group A patients was 4.33 ± 0.98 h versus 9.88 ± 0.90 h in Group B patients. Likewise, the difference in mean FLACC score of both the groups was also statistically significant, 7.21 ± 0.76 and 6.49 ± 1.72 in Group A and Group B, respectively.
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine as adjuvant to Bupivacaine increases duration of caudal analgesia and improves hemodynamic stability without an increase in adverse effects in children undergoing infraumbilical surgeries.
Keywords: Caudal block; dexmedetomidine; pediatric patients; postoperative analgesia.
Figures
References
-
- Hager H, Marhofer P, Sitzwohl C, Adler L, Kettner S, Semsroth M. Caudal clonidine prolongs analgesia from caudal S(+)-ketamine in children. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:1169–72. - PubMed
-
- Cook B, Grubb DJ, Aldridge LA, Doyle E. Comparison of the effects of adrenaline, clonidine and ketamine on the duration of caudal analgesia produced by bupivacaine in children. Br J Anaesth. 1995;75:698–701. - PubMed
-
- Singh R, Kumar N, Singh P. Randomized controlled trial comparing morphine or clonidine with bupivacaine for caudal analgesia in children undergoing upper abdominal surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2011;106:96–100. - PubMed
-
- Constant I, Gall O, Gouyet L, Chauvin M, Murat I. Addition of clonidine or fentanyl to local anaesthetics prolongs the duration of surgical analgesia after single shot caudal block in children. Br J Anaesth. 1998;80:294–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous