Sevoflurane in low-flow anesthesia using "equilibration point"
- PMID: 27212762
- PMCID: PMC4864709
- DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.172343
Sevoflurane in low-flow anesthesia using "equilibration point"
Abstract
Context: While giving low-flow anesthesia, it is a routine practice to give fixed duration of initial high-flow. This study was conducted to show the use of equilibration point as changeover point from initial high-flow to low-flow.
Aims: It was to compare the use of equilibration point, hemodynamics, end-tidal agent concentration, recovery time, and recovery score between isoflurane and sevoflurane.
Settings and design: It was a prospective randomized study conducted on 100 patients who were admitted for elective surgery expected to be < 2 h duration.
Materials and methods: Patients were randomly assigned to one of the two groups of 50 each. Group I received isoflurane and Group S sevoflurane as an inhalational agent.
Statistical analysis: The observations obtained in both the groups were recorded and compared. Analysis was done using unpaired t-test and Chi-square test.
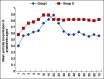
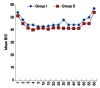
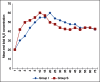
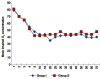
Results: Hemodynamic parameters were comparable in both the groups. The mean equilibration times obtained for sevoflurane and isoflurane were 8.22 ± 1.060 min and 17.24 ± 10.2 min, respectively. The drift in end-tidal agent concentration over time was less in sevoflurane group. Mean recovery time was 7.92 ± 1.56 min in the sevoflurane group and 12.89 ± 3.45 min in the isoflurane group (P = 0.001). There was no significant difference between intraoperative and postoperative complications.
Conclusion: Use of equilibration time of the volatile anesthetic agent as a changeover point, from high-flow to low-flow, can help us to use circle system with low-flow anesthesia in a more efficient way, especially with newer anesthetics such as sevoflurane.
Keywords: Equilibration time; low-flow; volatile anesthetic agent.
Figures
References
-
- Olympio MA. Modern Anesthesia Machines Offer New Safety Features. [Last accessed on 2013 Jul 31]. Available from: http://www.apsf.org/newsletters/html/2003/summer/machines.htm .
-
- Brockwell RC, Andrews JJ. Inhaled anesthetic delivery systems. In: Miller RD, editor. Miller's Anesthesia. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2009. pp. 667–718.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

