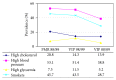
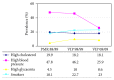
Trends of Prevalence of Uncontrolled Risk Factors for Cerebrocardiovascular Disease: Southern Italy from 1988/9 to 2008/9
- PMID: 27213054
- PMCID: PMC4860211
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6087981
Trends of Prevalence of Uncontrolled Risk Factors for Cerebrocardiovascular Disease: Southern Italy from 1988/9 to 2008/9
Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine the trends of cardiovascular risk factor prevalence between 1988/9 and 2008/9 in the 25-74-year-old population in an area of Southern Italy. We compared three cross-sectional studies conducted in random population samples, in 1988/9, 1998/9, and 2008/9 in Salerno, Italy. The methodology of data collection (lipid profile, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, glycaemia, and smoking) and conducting tests which the population underwent during the three phases was standardized and comparable. Prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and smoking was calculated and standardized for age. A total of 3491 subjects were included. From 1988/9 to 2008/9, in males, the prevalence of all four risk factors was reduced. In women, there was a clear reduction of hypertension, a similar prevalence of hypercholesterolemia, and an increase of smoking and diabetes. In the area of Salerno, our data confirm that the global prevalence of the major risk factors is decreasing in men, but their absolute values are still far from optimization. In women, diabetes and smoking showed a negative trend, therefore requiring targeted interventions. These data are now used as a base for executive targeted programs to improve prevention of cardiovascular disease in our community.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends in cardiovascular risk factor prevalence (1995-2000-2005) in northeastern Spain.Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007 Oct;14(5):653-9. doi: 10.1097/HJR.0b013e3281764429. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007. PMID: 17925624
-
Correlation between body mass index and others risk factors for cardiovascular disease in women compared with men.Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2003 Dec;60(4):295-300. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2003. PMID: 15061604
-
[The VIP Project: prevalence of risk factors for ischemic cardiopathy in an area of Campania].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2001 Nov;2(11):1201-8. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11775412 Clinical Trial. Italian.
-
[Asymptomatic arteriopathy of the lower limbs. Prevalence and risk factors in a population of southern Italy].Minerva Cardioangiol. 1993 Apr;41(4):133-8. Minerva Cardioangiol. 1993. PMID: 8332269 Italian.
-
[Cardiovascular risk and cardiometabolic risk: an epidemiological evaluation].G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008 Apr;9(4 Suppl 1):6S-17S. G Ital Cardiol (Rome). 2008. PMID: 18773746 Review. Italian.
References
-
- Huffman M. D., Capewell S., Ning H., Shay C. M., Ford E. S., Lloyd-Jones D. M. Cardiovascular health behavior and health factor changes (1988–2008) and projections to 2020: results from the national health and nutrition examination surveys. Circulation. 2012;125(21):2595–2602. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.111.070722. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Helis E., Augustincic L., Steiner S., Chen L., Turton P., Fodor J. G. Time trends in cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in the “old” and “new” European Union countries. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation. 2011;18(3):347–359. doi: 10.1177/1741826710389361. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Research Group ATS-RF2 CNR. The risk factors of atherosclerosis in Italy. Phase A of the project CNR-RF2. Giornale Italiano di Cardiologia. 1980;11(supplement 3):1–184.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources