Comparative Proteomics Reveals Dysregulated Mitochondrial O-GlcNAcylation in Diabetic Hearts
- PMID: 27213235
- PMCID: PMC7814404
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00250
Comparative Proteomics Reveals Dysregulated Mitochondrial O-GlcNAcylation in Diabetic Hearts
Abstract
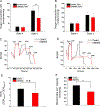
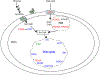
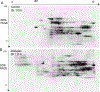
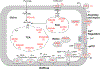
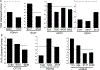
O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc), a post-translational modification on serine and threonine residues of many proteins, plays crucial regulatory roles in diverse biological events. As a nutrient sensor, O-GlcNAc modification (O-GlcNAcylation) on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins underlies the pathology of diabetic complications including cardiomyopathy. However, mitochondrial O-GlcNAcylation, especially in response to chronic hyperglycemia in diabetes, has been poorly explored. We performed a comparative O-GlcNAc profiling of mitochondria from control and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat hearts by using an improved β-elimination/Michael addition with isotopic DTT reagents (BEMAD) followed by tandem mass spectrometric analysis. In total, 86 mitochondrial proteins, involved in diverse pathways, were O-GlcNAcylated. Among them, many proteins have site-specific alterations in O-GlcNAcylation in response to diabetes, which suggests that protein O-GlcNAcylation is a novel layer of regulation mediating adaptive changes in mitochondrial metabolism during the progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: O-GlcNAcome; O-GlcNAcylation; diabetic cardiomyopathy; mass spectrometry; mitochondria; proteomics; pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Figures
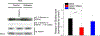
References
-
- Torres CR; Hart GW Topography and polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes. Evidence for O-linked GlcNAc. J. Biol. Chem 1984, 259, 3308–3317. - PubMed
-
- Holt GD; Hart GW The subcellular distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine moieties: Localization of a novel protein-saccharide linkage, O-linked GlcNAc. J. Biol. Chem 1986, 261, 8049–8057. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZV; Deng Y; Gao N; Pedrozo Z; Li DL; Morales CR; Criollo A; Luo X; Tan W; Jiang N; Lehrman MA; Rothermel BA; Lee AH; Lavandero S; Mammen PP; Ferdous A; Gillette TG; Scherer PE; Hill JA Spliced X-box binding protein 1 couples the unfolded protein response to hexosamine biosynthetic pathway. Cell 2014, 156, 1179–1192. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

