Low-Molecular Weight Polyethylenimine Modified with Pluronic 123 and RGD- or Chimeric RGD-NLS Peptide: Characteristics and Transfection Efficacy of Their Complexes with Plasmid DNA
- PMID: 27213305
- PMCID: PMC6273895
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21050655
Low-Molecular Weight Polyethylenimine Modified with Pluronic 123 and RGD- or Chimeric RGD-NLS Peptide: Characteristics and Transfection Efficacy of Their Complexes with Plasmid DNA
Abstract
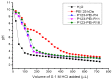
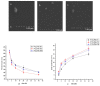
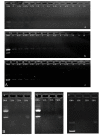
To solve the problem of transfection efficiency vs. cytotoxicity and tumor-targeting ability when polyethylenimine (PEI) was used as a nonviral gene delivery vector, new degradable PEI polymers were synthesized via cross-linking low-molecular-weight PEI with Pluronic P123 and then further coupled with a targeting peptide R4 (RGD) and a bifunctional R11 (RGD-NLS), which were termed as P123-PEI-R4 and P123-PEI-R11, respectively. Agarose gel electrophoresis showed that both P123-PEI-R4 and P123-PEI-R11 efficaciously condense plasmid DNA at a polymer-to-pDNA w/w ratio of 3.0 and 0.4, respectively. The polyplexes were stable in the presence of serum and could protect plasmid DNA against DNaseI. They had uniform spherical nanoparticles with appropriate sizes around 100-280 nm and zeta-potentials about +40 mV. Furthermore, in vitro experiments showed that these polyplexes had lower cytotoxicity at any concentration compared with PEI 25 kDa, thus giving promise to high transfection efficiency as compared with another P123-PEI derivate conjugated with trifunctional peptide RGD-TAT-NLS (P123-PEI-R18). More importantly, compared with the other polymers, P123-PEI-R11 showed the highest transfection efficiency with relatively lower cytotoxicity at any concentration, indicating that the new synthetic polymer P123-PEI-R11 could be used as a safe and efficient gene deliver vector.
Keywords: RGD; nuclear localization signal; physico-chemical properties; polycations; transfection efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Biodegradable Polyethylenimine-Based Vector Modified by Trifunctional Peptide R18 for Enhancing Gene Transfection Efficiency In Vivo.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0166673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166673. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27935984 Free PMC article.
-
Degradable polyethylenimine derivate coupled to a bifunctional peptide R13 as a new gene-delivery vector.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1149-62. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S28819. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22412301 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethylenimine derivate conjugated with RGD-TAT-NLS as a novel gene vector.Biomed Mater Eng. 2014;24(6):1933-9. doi: 10.3233/BME-141002. Biomed Mater Eng. 2014. PMID: 25226889
-
Polyethyleneimine-Based Nanocarriers for Gene Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(42):6140-56. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666151027152907. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26503146 Review.
-
Poly(ethylenimine) and its role in gene delivery.J Control Release. 1999 Aug 5;60(2-3):149-60. doi: 10.1016/s0168-3659(99)00090-5. J Control Release. 1999. PMID: 10425321 Review.
Cited by
-
Addition of free poloxamer 407 to a new gene vector P407-PEI-K12 solution forms a sustained-release in situ hypergel that enhances cell transfection and extends gene expression.Oncol Lett. 2019 Mar;17(3):3085-3096. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.9944. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30867738 Free PMC article.
-
ROS responsive polyethylenimine-based fluorinated polymers for enhanced transfection efficiency and lower cytotoxicity.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Jul 29;22(4):593-607. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.6704. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35531984 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Non-Viral Vectors Based on Pluronic® F68PEI with Application in Oncology Field.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 5;14(23):5315. doi: 10.3390/polym14235315. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501709 Free PMC article.
-
Stimuli-Regulated Smart Polymeric Systems for Gene Therapy.Polymers (Basel). 2017 Apr 24;9(4):152. doi: 10.3390/polym9040152. Polymers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30970831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pH- and Bioreducible Cationic Copolymer with Amino Acids and Piperazines for Adenovirus Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 9;14(3):597. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030597. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35335972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tripathi S.K., Gupta S., Gupta K.C., Kumar P. Efficient DNA and siRNA delivery with biodegradable cationic hyaluronic acid conjugates. R. Soc. Chem. 2013;3:15687–15697. doi: 10.1039/c3ra42013b. - DOI
-
- Perez F.C., Carrion B., Cena V. The use of nanoparticles for gene therapy in the nervous system. J. Dis. 2012;31:697–710. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

