Novel Radioligands for Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase Imaging with Positron Emission Tomography: An Update on Developments Since 2012
- PMID: 27213312
- PMCID: PMC6273803
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21050650
Novel Radioligands for Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase Imaging with Positron Emission Tomography: An Update on Developments Since 2012
Abstract
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are a class of intracellular enzymes that inactivate the secondary messenger molecules, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Thus, PDEs regulate the signaling cascades mediated by these cyclic nucleotides and affect fundamental intracellular processes. Pharmacological inhibition of PDE activity is a promising strategy for treatment of several diseases. However, the role of the different PDEs in related pathologies is not completely clarified yet. PDE-specific radioligands enable non-invasive visualization and quantification of these enzymes by positron emission tomography (PET) in vivo and provide an important translational tool for elucidation of the relationship between altered expression of PDEs and pathophysiological effects as well as (pre-)clinical evaluation of novel PDE inhibitors developed as therapeutics. Herein we present an overview of novel PDE radioligands for PET published since 2012.
Keywords: PDE inhibitors; PDE radioligands; cyclic nucleotide signaling; imaging; phosphodiesterases; positron emission tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




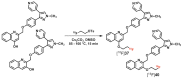
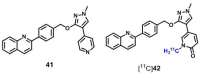

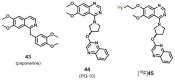
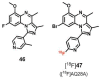
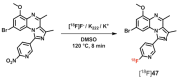
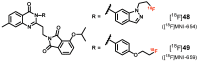
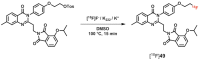
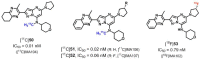


Similar articles
-
Challenges on Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases Imaging with Positron Emission Tomography: Novel Radioligands and (Pre-)Clinical Insights since 2016.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 7;22(8):3832. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083832. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carboxyamidotriazole: a novel inhibitor of both cAMP-phosphodiesterases and cGMP-phosphodiesterases.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan 5;746:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.10.018. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25446933
-
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) in human osteoblastic cells; the effect of PDE inhibition on cAMP accumulation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2005;10(2):305-19. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2005. PMID: 16010295
-
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors: novel therapeutic agents for progressive renal disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2007 Jan;232(1):38-51. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2007. PMID: 17202584 Review.
-
Recent advances in positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracers for imaging phosphodiesterases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(11):1224-36. doi: 10.2174/156802612800672853. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22571785 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Imaging of Hydrolytic Enzymes Using PET and SPECT.Mol Imaging. 2017 Jan-Dec;16:1536012117717852. doi: 10.1177/1536012117717852. Mol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28927325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In the Brain of Phosphodiesterases: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Schizophrenia.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2025 Feb 28;23(1):15-31. doi: 10.9758/cpn.24.1229. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39820109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Repertoire of Small-Molecule PET Probes for Neuroinflammation Imaging: Challenges and Opportunities beyond TSPO.J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 23;64(24):17656-17689. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01571. Epub 2021 Dec 14. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34905377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Empirical Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Equation Assists the Discovery of High-Affinity Phosphodiesterase 4D Inhibitors as Leads to PET Radioligands.J Med Chem. 2023 Jan 26;66(2):1543-1561. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01745. Epub 2023 Jan 6. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36608175 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Quantification of Phosphodiesterase-4D in Monkey Brain with PET and 11C-Labeled Radioligands That Avoid Radiometabolite Contamination.J Nucl Med. 2024 May 1;65(5):788-793. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.266750. J Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 38423785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wahl R.L., Wagner H.N. Principles and Practice of PET and PET/CT. 2nd ed. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2009. p. 729.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

