Positively Charged Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and Their Effect on the Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs
- PMID: 27213324
- PMCID: PMC6273568
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21050672
Positively Charged Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and Their Effect on the Dissolution of Poorly Soluble Drugs
Abstract
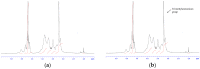
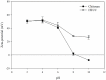
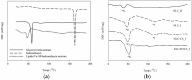
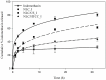
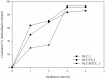
The objective of this study is to develop suitable formulations to improve the dissolution rate of poorly water soluble drugs. We selected lipid-based formulation as a drug carrier and modified the surface using positively charged chitosan derivative (HTCC) to increase its water solubility and bioavailability. Chitosan and HTCC-coated lipid particles had higher zeta-potential values than uncoated one over the whole pH ranges and improved encapsulation efficiency. In vitro drug release showed that all NLC formulations showed higher in vitro release efficiency than drug particle at pH 7.4. Furthermore, NLC formulation prepared with chitosan or HTCC represented good sustained release property. The results indicate that chitosan and HTCC can be excellent formulating excipients of lipid-based delivery carrier for improving poorly water soluble drug delivery.
Keywords: N-(2-hydroxy)propyl-3-trimethyl ammonium chitosan chloride; in vitro release; indomethacin; nanostructured lipid nanocarrier; poorly water soluble drug.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel oral delivery system consisting in "drug-in cyclodextrin-in nanostructured lipid carriers" for poorly water-soluble drug: vinpocetine.Int J Pharm. 2014 Apr 25;465(1-2):90-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Int J Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24530388
-
Preparation and characterization of dutasteride-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers coated with stearic acid-chitosan oligomer for topical delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017 Aug;117:372-384. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017. PMID: 28412472
-
Synthesis and characterization of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt and its application as drug carrier for ribavirin.Drug Deliv. 2014 Nov;21(7):548-52. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2013.853708. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24215307
-
Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: A review emphasizing on particle structure and drug release.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 Dec;133:285-308. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.10.017. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 30463794 Review.
-
Lipid-based systems as a promising approach for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.Acta Pharm. 2013 Dec;63(4):427-45. doi: 10.2478/acph-2013-0040. Acta Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24451070 Review.
Cited by
-
Studies on Intermolecular Interaction of N-Glycidyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Modified Chitosan/N,N-Dimethyl-N-dodecyl-N-(2,3-epoxy propyl) Ammonium Chloride and Curcumin Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 10;14(10):1936. doi: 10.3390/polym14101936. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631818 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of atorvastatin and quercetin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles using Box-Behnken design.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024 Jul 14;19(17):1541-1555. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2364585. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39012199 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation of lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles of the phytochemical Fisetin and its in vivo assessment against severe acute pancreatitis.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 4;13(1):19110. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46215-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37925581 Free PMC article.
-
Virgin Coconut Oil-based Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Improves the Hypolipidemic Effect of Rosuvastatin.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Aug 5;19:7945-7961. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S463750. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39130688 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Nanomedicines for Targeted Therapy of Bladder Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 16;12:778973. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.778973. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arrunategui L.B., Silva-Barcellos N.M., Bellavinha K.R., Ev L.S., de Souza J. Biopharmaceutics classification system: importance and inclusion in biowaiver guidance. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015;51:143–154. doi: 10.1590/S1984-82502015000100015. - DOI
-
- Nayak A.K., Maji R., Das B. Gastroretentive drug delivery systems: A review. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2010;3:2–10.
-
- Kobayashi K., Wei J., Iida R., Ijiro K., Niikura K. Surface engineering of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Polym. J. 2014;46:460–468. doi: 10.1038/pj.2014.40. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

