Marine Invertebrate Metabolites with Anticancer Activities: Solutions to the "Supply Problem"
- PMID: 27213412
- PMCID: PMC4882572
- DOI: 10.3390/md14050098
Marine Invertebrate Metabolites with Anticancer Activities: Solutions to the "Supply Problem"
Abstract
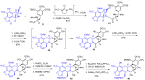
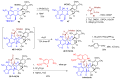
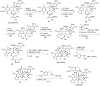
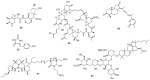
Marine invertebrates provide a rich source of metabolites with anticancer activities and several marine-derived agents have been approved for the treatment of cancer. However, the limited supply of promising anticancer metabolites from their natural sources is a major hurdle to their preclinical and clinical development. Thus, the lack of a sustainable large-scale supply has been an important challenge facing chemists and biologists involved in marine-based drug discovery. In the current review we describe the main strategies aimed to overcome the supply problem. These include: marine invertebrate aquaculture, invertebrate and symbiont cell culture, culture-independent strategies, total chemical synthesis, semi-synthesis, and a number of hybrid strategies. We provide examples illustrating the application of these strategies for the supply of marine invertebrate-derived anticancer agents. Finally, we encourage the scientific community to develop scalable methods to obtain selected metabolites, which in the authors' opinion should be pursued due to their most promising anticancer activities.
Keywords: discodermolide; eribulin; frondoside A; monanchocidin A; mycalamide A; phenylmethylene hydantoin; spongistatin 1; stelletin A; trabectedin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomaterials and Bioactive Natural Products from Marine Invertebrates: From Basic Research to Innovative Applications.Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 22;20(4):219. doi: 10.3390/md20040219. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Seabed to Bedside: A Review on Promising Marine Anticancer Compounds.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 6;10(2):248. doi: 10.3390/biom10020248. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32041255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highlights of marine invertebrate-derived biosynthetic products: their biomedical potential and possible production by microbial associants.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Nov 15;19(22):6658-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.07.017. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21835627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine microorganism-invertebrate assemblages: perspectives to solve the "supply problem" in the initial steps of drug discovery.Mar Drugs. 2014 Jun 30;12(7):3929-52. doi: 10.3390/md12073929. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24983638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update.Mar Drugs. 2018 Nov 26;16(12):467. doi: 10.3390/md16120467. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30486251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Compounds from Marine Sponges: Fundamentals and Applications.Mar Drugs. 2021 Apr 27;19(5):246. doi: 10.3390/md19050246. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33925365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Diversity and Biotechnological Potential of Cultured and Uncultured Coral-Associated Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2021 Oct 27;9(11):2235. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112235. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34835361 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Technologies for Large Scale Supply of Marine Drugs.Mar Drugs. 2025 Feb 7;23(2):69. doi: 10.3390/md23020069. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Phylum Bryozoa: From Biology to Biomedical Potential.Mar Drugs. 2020 Apr 9;18(4):200. doi: 10.3390/md18040200. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32283669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double the Chemistry, Double the Fun: Structural Diversity and Biological Activity of Marine-Derived Diketopiperazine Dimers.Mar Drugs. 2019 Sep 27;17(10):551. doi: 10.3390/md17100551. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31569621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

