Tocilizumab in Autoimmune Encephalitis Refractory to Rituximab: An Institutional Cohort Study
- PMID: 27215218
- PMCID: PMC5081109
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-016-0442-6
Tocilizumab in Autoimmune Encephalitis Refractory to Rituximab: An Institutional Cohort Study
Abstract
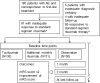
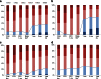
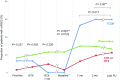
A considerable portion of autoimmune encephalitis (AE) does not respond to conventional immunotherapies and subsequently has poor outcomes. We aimed to determine the efficacy of tocilizumab, an anti-interleukin-6 antibody, in rituximab-refractory AE compared with other treatment options. From an institutional cohort of AE, 91 patients with inadequate clinical response to first-line immunotherapy and following rituximab were retrospectively reviewed. Patients were grouped according to their further immunotherapy strategies. Thirty (33.0 %) patients were included in the tocilizumab group, 31 (34.0 %) in the additional rituximab group, and 30 (33.0 %) in the observation group. Outcomes were defined as the favorable modified Rankin Scale scores (≤2) at 1 and 2 months from the initiation of each treatment strategy and at the last follow-up. Favorable clinical response (improvement of the modified Rankin Scale scores by ≥ 2 points or achievement of the mRS scores ≤ 2) at the last follow-up was also analyzed. The tocilizumab group showed more frequent favorable mRS scores at 2 months from treatment initiation and at the last follow-up compared with those at the relevant time points of the remaining groups. The majority (89.5 %) of the patients with clinical improvement at 1 month from tocilizumab treatment maintained a long-term favorable clinical response. No serious adverse effects of rituximab or tocilizumab were reported. Therefore, we suggest that tocilizumab might be a good treatment strategy for treating AE refractory to conventional immunotherapies and rituximab. The tocilizumab-mediated clinical improvement manifests as early at 1 month after treatment initiation.
Keywords: Autoimmune disorders; encephalitis; immunotherapy; prognosis; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical Standards Conflicts of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Interleukin-6 Blockade as Rescue Therapy in Autoimmune Encephalitis.Neurotherapeutics. 2016 Oct;13(4):821-823. doi: 10.1007/s13311-016-0471-1. Neurotherapeutics. 2016. PMID: 27530677 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Rituximab treatment for autoimmune limbic encephalitis in an institutional cohort.Neurology. 2016 May 3;86(18):1683-91. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002635. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27037228
-
Tocilizumab in Refractory Autoimmune Encephalitis: A Series of Pediatric Cases.Pediatr Neurol. 2018 Sep;86:66-68. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Pediatr Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30177347
-
Teratoma Removal, Steroid, IVIG, Rituximab and Tocilizumab (T-SIRT) in Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jan;18(1):474-487. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00921-7. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 32880854 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of rituximab in autoimmune encephalitis: A meta-analysis.Acta Neurol Scand. 2020 Nov;142(5):449-459. doi: 10.1111/ane.13291. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Acta Neurol Scand. 2020. PMID: 32484900 Review.
-
[An Update on Therapeutic Management in Autoimmune Encephalitis].Brain Nerve. 2023 May;75(5):479-484. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416202362. Brain Nerve. 2023. PMID: 37194516 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Neuroimaging characteristics may aid in diagnosis, subtyping, and prognosis in autoimmune encephalitis.Neurol Sci. 2023 Apr;44(4):1327-1340. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06523-9. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36481972
-
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals cell type-specific immune regulation associated with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in humans.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 2;13:1075675. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1075675. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36544777 Free PMC article.
-
Case report of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in a 24-year-old female: an uncommon presentation.Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg. 2022;58(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s41983-022-00512-7. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35761962 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Features and Therapeutic Effects of Anti-leucine-rich Glioma Inactivated 1 Encephalitis: A Systematic Review.Front Neurol. 2022 Jan 12;12:791014. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.791014. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35095736 Free PMC article.
-
High albumin level is a predictor of favorable response to immunotherapy in autoimmune encephalitis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):1012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19490-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gable MS, Sheriff H, Dalmau J, Tilley DH, Glaser CA. The frequency of autoimmune N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis surpasses that of individual viral etiologies in young individuals enrolled in the California Encephalitis Project. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:899–904. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir1038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

