SMN and coilin negatively regulate dyskerin association with telomerase RNA
- PMID: 27215323
- PMCID: PMC4920197
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.018804
SMN and coilin negatively regulate dyskerin association with telomerase RNA
Abstract
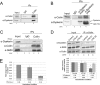
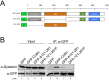
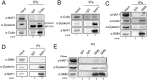
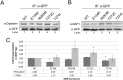
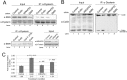
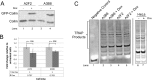
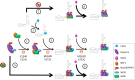
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein comprising telomerase RNA and associated proteins. The formation of the telomerase holoenzyme takes place in the Cajal body (CB), a subnuclear domain that participates in the formation of ribonucleoproteins. CBs also contribute to the delivery of telomerase to telomeres. The protein WRAP53 is enriched within the CB and is instrumental for the targeting of telomerase RNA to CBs. Two other CB proteins, SMN and coilin, are also suspected of taking part in some aspect of telomerase biogenesis. Here we demonstrate newly discovered associations between SMN and coilin with telomerase components, and further show that reduction of SMN or coilin is correlated with increased association of telomerase RNA with one these components, dyskerin. These findings argue that SMN and coilin may negatively regulate the formation of telomerase. Furthermore, clinically defined SMN mutants found in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy are altered in their association with telomerase complex proteins. Additionally, we observe that a coilin derivative also associates with dyskerin, and the amount of this protein in the complex is regulated by SMN, WRAP53 and coilin levels. Collectively, our findings bolster the link between SMN, coilin and the coilin derivative in the biogenesis of telomerase.
Keywords: Cajal body; Coilin; SMN; Telomerase.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

