Circulating secretory IgA antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides in early rheumatoid arthritis associate with inflammatory activity and smoking
- PMID: 27215344
- PMCID: PMC4877943
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-016-1014-1
Circulating secretory IgA antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides in early rheumatoid arthritis associate with inflammatory activity and smoking
Abstract
Background: A possible association between mucosal immunization and inflammation, as well as the initiation and propagation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), is attracting renewed interest. The aim of this study was to evaluate the possible occurrence and clinical correlations of circulating secretory immunoglobulin A (SIgA) antibodies against the second-generation cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) among patients with recent-onset RA followed prospectively over 3 years.
Methods: Baseline serum samples from 636 patients with recent-onset RA were analyzed for SIgA anti-CCP antibodies by using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a secondary antibody directed against secretory component. SIgA anti-CCP status at baseline was analyzed in relation to smoking, HLA-DRB1/shared epitope (SE), and the disease course over 3 years. Significant findings were evaluated in regression analysis that included age, sex, smoking, and SE.
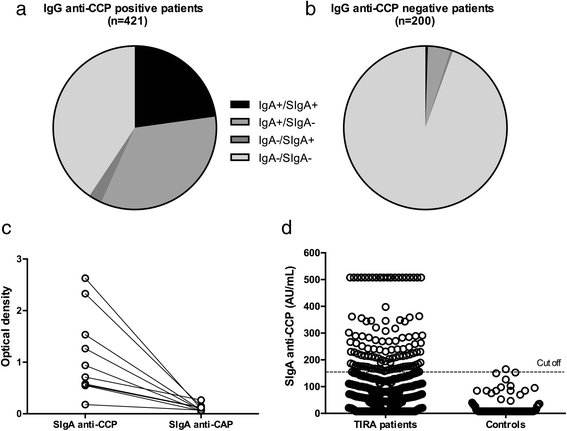
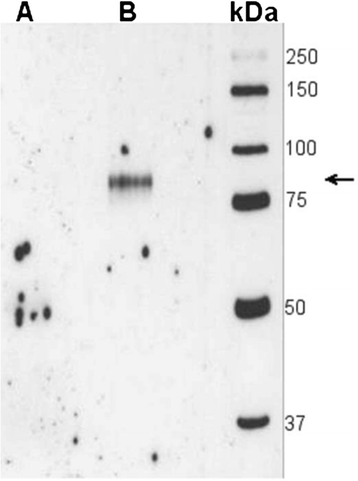
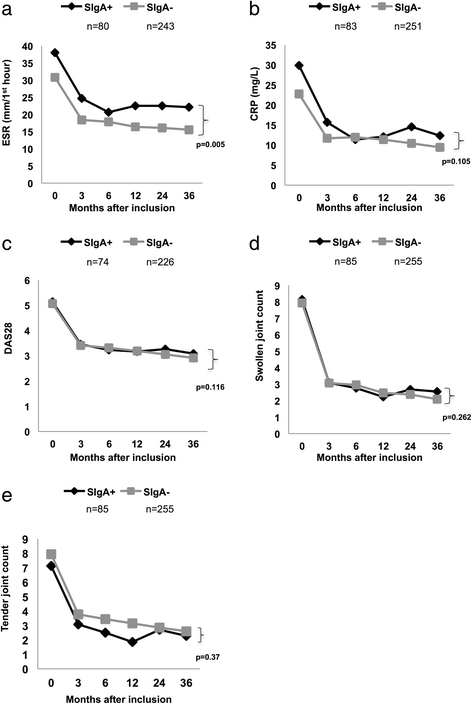
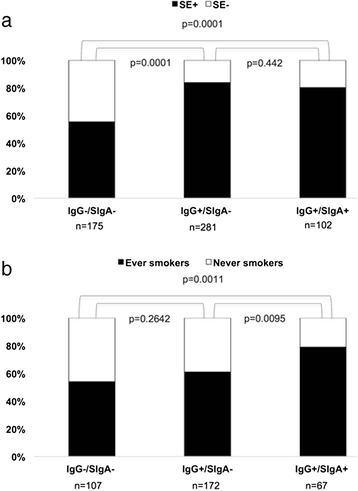
Results: Seventeen percent of the patients tested positive for circulating SIgA anti-CCP, and the occurrence was confirmed by detection of secretory component in an affinity-purified IgA anti-CCP fraction. SIgA anti-CCP positivity at baseline was associated with slightly higher baseline erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (mean 38 vs. 31 mm/first hour, p = 0.004) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (mean 30 vs. 23 mg/L, p = 0.047). During follow-up, SIgA anti-CCP-positive patients had a higher mean AUC regarding ESR (adjusted p = 0.003), although there were no significant differences regarding CRP, tender and swollen joint counts, or radiological joint damage (median Larsen progression 1.0 vs. 1.0, p = 0.22). SIgA anti-CCP was associated significantly with smoking (79 % ever smokers among SIgA anti-CCP-positive patients vs. 59 % in SIgA anti-CCP-negative patients, adjusted OR 2.19, 95 % CI 1.01-4.37, p = 0.027) but not with carriage of the SE (80 % vs. 73 %, p = 0.62).
Conclusions: Circulating SIgA anti-CCP, which is present in a subgroup of patients with early RA, is not related to SE, but it is environmentally linked to cigarette smoking. This finding strengthens the hypothesis that immunization against citrullinated peptides and/or proteins may occur at mucosal surfaces of the airways. Analysis of SIgA antibodies in serum may be a convenient and more versatile means to investigate the "mucosal connection" in RA compared with analyses in mucosal fluid samples.
Keywords: Anticitrullinated protein antibodies; Mucosal immunity; Rheumatoid arthritis; Secretory immunoglobulin A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations with smoking and shared epitope differ between IgA- and IgG-class antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides in early rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67(8):2032-7. doi: 10.1002/art.39170. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25916813
-
Immunoglobulin (Ig)G1 and IgG4 anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) associate with shared epitope, whereas IgG2 anti-CCP associates with smoking in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis (the Swedish TIRA project).Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Apr;188(1):53-62. doi: 10.1111/cei.12901. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27859022 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of anticitrullinated protein antibody reactivities in a subset of anti-CCP-negative rheumatoid arthritis: association with cigarette smoking and HLA-DRB1 'shared epitope' alleles.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Mar;74(3):579-86. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203915. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24297382 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-environmental interaction between smoking and shared epitope on the development of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2014 Jun;17(5):528-35. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12307. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 24618101 Review.
-
Redefining the HLA and RA association: to be or not to be anti-CCP positive.J Autoimmun. 2005;25 Suppl:21-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2005.09.005. Epub 2005 Oct 27. J Autoimmun. 2005. PMID: 16257178 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Factors in PAD2 (PADI2) and PAD4 (PADI4) Are Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease Susceptibility in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Cells. 2023 Sep 8;12(18):2235. doi: 10.3390/cells12182235. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37759458 Free PMC article.
-
Anticyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies 3.1 and Anti-CCP-IgA Are Associated with Increasing Age in Individuals Without Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2019 Dec;46(12):1556-1559. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180897. Epub 2019 Apr 15. J Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30988128 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-phospholipid Antibodies and Smoking: An Overview.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Aug;53(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8565-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27377297 Review.
-
Mucosa-Environment Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2019 Jul 10;8(7):700. doi: 10.3390/cells8070700. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31295951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticitrullinated protein antibodies: origin and role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017 Jan;29(1):57-64. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000356. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27755123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kroot EJ, de Jong BA, van Leeuwen MA, Swinkels H, van den Hoogen FH, van ’t Hof M, et al. The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1831–5. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200008)43:8<1831::AID-ANR19>3.0.CO;2-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

