A bundled care approach to patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis improves transplant-free survival
- PMID: 27215501
- PMCID: PMC4879776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.04.010
A bundled care approach to patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis improves transplant-free survival
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic lung disease with poor prognosis and limited therapeutic options. The 2011 ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT consensus statement provided a number of recommendations for the management of IPF patients. The primary objective of this study was to determine if "bundling" these recommendations in the management of patients with IPF impacts clinical outcomes.
Methods: We conducted a single center, retrospective cohort study of 284 patients diagnosed with IPF. The proposed bundle of care (BOC) components were: (1) visits to a specialized interstitial lung diseases clinic with evaluation of pulmonary function tests at least twice yearly; (2) referral to pulmonary rehabilitation yearly; (3) timed walk test yearly; (4) echocardiogram yearly; and (5) gastroesophageal reflux therapy. Each component of the BOC was given a score of "1" per year of follow up, and the average sum of the scores (ranging from 0 to 5) was determined for the entire period of follow-up (BOCS), as well as during the first year of follow-up (BOCY1). The primary outcome measure was transplant-free survival.
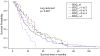
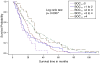
Results: Age, gender, smoking status, BMI, %FVC, %DLCO did not differ between levels of BOCS and BOCY1. Lowest BOCS (≤1) was associated with a lower transplant-free survival independent of age and %FVC compared to patients with the highest BOCS (>4) (HR 2.274, CI 1.12-4.64, p = 0.024). Lower BOCY1 was associated with a higher risk for transplant or death independent of age and %FVC in comparison to patients with highest BOCY1 (≤1 vs. >4, HR 2.23, p = 0.014; >1 to 2 vs. >4, HR 1.87, p = 0.011; >2 to 3 vs. >4, HR 1.72, p = 0.019).
Conclusion: IPF patients with higher BOC scores had improved transplant-free survival. Prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and determine the best strategies for the management of patients with IPF.
Keywords: Bundled care; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Transplant-free survival.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, Lynch DA, Ryu JH, Swigris JJ, Wells AU, Ancochea J, Bouros D, Carvalho C, Costabel U, Ebina M, Hansell DM, Johkoh T, Kim DS, King TE, Jr, Kondoh Y, Myers J, Muller NL, Nicholson AG, Richeldi L, Selman M, Dudden RF, Griss BS, Protzko SL, Schunemann HJ Fibrosis AEJACoIP. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:788–824. - PMC - PubMed
-
- King TE, Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM, Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, Lederer DJ, Nathan SD, Pereira CA, Sahn SA, Sussman R, Swigris JJ, Noble PW, Group AS. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2083–2092. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, Hansell DM, Inoue Y, Kim DS, Kolb M, Nicholson AG, Noble PW, Selman M, Taniguchi H, Brun M, Le Maulf F, Girard M, Stowasser S, Schlenker-Herceg R, Disse B, Collard HR Investigators IT. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2071–2082. - PubMed
-
- Robb E, Jarman B, Suntharalingam G, Higgens C, Tennant R, Elcock K. Using care bundles to reduce in-hospital mortality: quantitative survey. BMJ. 2010;340:c1234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

