Detection of the mcr-1 Colistin Resistance Gene in Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae from Different Hospitals in China
- PMID: 27216058
- PMCID: PMC4958199
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00440-16
Detection of the mcr-1 Colistin Resistance Gene in Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae from Different Hospitals in China
Abstract
The spread of the plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene, mcr-1, into carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) clinical isolates poses a significant threat to global health. Here we report the identification of three mcr-1-harboring carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli strains, collected from three patients in two provinces in China. Our results show that mcr-1-harboring CRE strains have started to spread in different hospitals in China. In addition, this report presents the first description of chromosomal integration of mcr-1 into a carbapenem-resistant E. coli strain.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
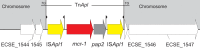
References
-
- Liu YY, Wang Y, Walsh TR, Yi LX, Zhang R, Spencer J, Doi Y, Tian G, Dong B, Huang X, Yu LF, Gu D, Ren H, Chen X, Lv L, He D, Zhou H, Liang Z, Liu JH, Shen J. 2016. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: a microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect Dis 16:161–168. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00424-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li A, Yang Y, Miao M, Chavda KD, Mediavilla JR, Xie X, Feng P, Tang YW, Kreiswirth BN, Chen L, Du H. 18 April 2016. Complete sequences of mcr-1-harboring plasmids from extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)- and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE). Antimicrob Agents Chemother doi:10.1128/AAC.00550-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, Harbarth S, Hindler JF, Kahlmeter G, Olsson-Liljequist B, Paterson DL, Rice LB, Stelling J, Struelens MJ, Vatopoulos A, Weber JT, Monnet DL. 2012. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 18:268–281. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

