Associated disease risk from the introduced generalist pathogen Sphaerothecum destruens: management and policy implications
- PMID: 27216376
- PMCID: PMC4926270
- DOI: 10.1017/S003118201600072X
Associated disease risk from the introduced generalist pathogen Sphaerothecum destruens: management and policy implications
Abstract
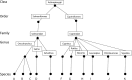
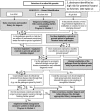
The rosette agent Sphaerothecum destruens is a novel pathogen, which is currently believed to have been introduced into Europe along with the introduction of the invasive fish topmouth gudgeon Pseudorasbora parva (Temminck & Schlegel, 1846). Its close association with P. parva and its wide host species range and associated host mortalities, highlight this parasite as a potential source of disease emergence in European fish species. Here, using a meta-analysis of the reported S. destruens prevalence across all reported susceptible hosts species; we calculated host-specificity providing support that S. destruens is a true generalist. We have applied all the available information on S. destruens and host-range to an established framework for risk-assessing non-native parasites to evaluate the risks posed by S. destruens and discuss the next steps to manage and prevent disease emergence of this generalist parasite.
Keywords: Europe; Pseudorasbora parva; aquatic ecosystems; biodiversity threat; disease emergence; topmouth gudgeon.
Figures
References
-
- Andreou D., Hussey M., Griffiths S. W. and Gozlan R. E. (2011). Influence of host reproductive state on Sphaerothecum destruens prevalence and infection level. Parasitology 138, 26–34. - PubMed
-
- Andreou D., Gozlan R. E. and Paley R. (2009). Temperature influence on production and longevity of Sphaerothecum destruens’ zoospores. Journal of Parasitology 95, 1539–1541. - PubMed
-
- Arkush K. D., Frasca S. and Hedrick R. P. (1998). Pathology associated with the rosette agent, a systemic protist infecting salmonid fishes. Journal ofAquatic Animal Health 10, 1–11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

