Final 5-Year Study Results of DASISION: The Dasatinib Versus Imatinib Study in Treatment-Naïve Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Trial
- PMID: 27217448
- PMCID: PMC5118045
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.8899
Final 5-Year Study Results of DASISION: The Dasatinib Versus Imatinib Study in Treatment-Naïve Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Trial
Abstract
Purpose: We report the 5-year analysis from the phase III Dasatinib Versus Imatinib Study in Treatment-Naïve Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients (DASISION) trial, evaluating long-term efficacy and safety outcomes of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase (CP) treated with dasatinib or imatinib.
Patients and methods: Patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP were randomly assigned to receive dasatinib 100 mg once daily (n = 259) or imatinib 400 mg once daily (n = 260).
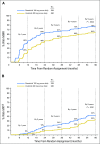
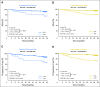
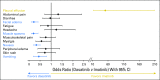
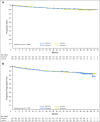
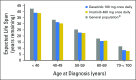
Results: At the time of study closure, 61% and 63% of dasatinib- and imatinib-treated patients remained on initial therapy, respectively. Cumulative rates of major molecular response and molecular responses with a 4.0- or 4.5-log reduction in BCR-ABL1 transcripts from baseline by 5 years remained statistically significantly higher for dasatinib compared with imatinib. Rates for progression-free and overall survival at 5 years remained high and similar across treatment arms. In patients who achieved BCR-ABL1 ≤ 10% at 3 months (dasatinib, 84%; imatinib, 64%), improvements in progression-free and overall survival and lower rates of transformation to accelerated/blast phase were reported compared with patients with BCR-ABL1 greater than 10% at 3 months. Transformation to accelerated/blast phase occurred in 5% and 7% of patients in the dasatinib and imatinib arms, respectively. Fifteen dasatinib-treated and 19 imatinib-treated patients had BCR-ABL1 mutations identified at discontinuation. There were no new or unexpected adverse events identified in either treatment arm, and pleural effusion was the only drug-related, nonhematologic adverse event reported more frequently with dasatinib (28% v 0.8% with imatinib). First occurrences of pleural effusion were reported with dasatinib, with the highest incidence in year 1. Arterial ischemic events were uncommon in both treatment arms.
Conclusion: These final results from the DASISION trial continue to support dasatinib 100 mg once daily as a safe and effective first-line therapy for the long-term treatment of CML-CP.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHORS’ DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Disclosures provided by the authors are available with this article at www.jco.org. AUTHORS’ DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO’s conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or jco.ascopubs.org/site/ifc. Jorge E. Cortes Consulting or Advisory Role: ARIAD, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer Research Funding: ARIAD (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Teva (Inst) Giuseppe Saglio Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, ARIAD, Pfizer Hagop M. Kantarjian Research Funding: Pfizer (Inst), ARIAD, Amgen (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Novartis (Inst) Michele Baccarani Honoraria: Bristol-Myers Squibb Consulting or Advisory Role: Bristol-Myers Squibb Speakers’ Bureau: Bristol-Myers Squibb Jiří Mayer Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb Research Funding: Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb Concepción Boqué Honoraria: Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Neil P. Shah Research Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb, ARIAD, Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, Plexxikon Charles Chuah Honoraria: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis Luis Casanova No relationship to disclose Brigid Bradley-Garelik Employment: Bristol-Myers Squibb Stock or Other Ownership: Bristol-Myers Squibb George Manos Employment: Bristol-Myers Squibb Stock or Other Ownership: Bristol-Myers Squibb Andreas Hochhaus Honoraria: Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, ARIAD, Omniamed Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, ARIAD Research Funding: Novartis (Inst), Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), ARIAD (Inst), MSD Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, ARIAD
Figures

Comment in
-
How Does One Decide Which Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor To Use for the Initial Treatment of Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?J Clin Oncol. 2017 Feb 10;35(5):567. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.5940. Epub 2016 Nov 14. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29236617 No abstract available.
-
Reply to K.R. Hoffman.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Feb 10;35(5):567-568. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.2944. Epub 2016 Nov 14. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29236618 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, et al. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2260–2270. - PubMed
-
- Bristol-Myers Squibb: Sprycel (dasatinib) [prescribing information]. Princeton, NJ, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, 2015.
-
- Cortes JE, Hochhaus A, Kim DW, et al. Four-year (yr) follow-up of patients (pts) with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) receiving dasatinib or imatinib: Efficacy based on early response. Blood. 2013;122:653. (abstr)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

