Revealing a 5,000-y-old beer recipe in China
- PMID: 27217567
- PMCID: PMC4988576
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1601465113
Revealing a 5,000-y-old beer recipe in China
Abstract
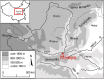
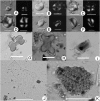
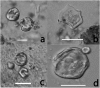
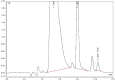
The pottery vessels from the Mijiaya site reveal, to our knowledge, the first direct evidence of in situ beer making in China, based on the analyses of starch, phytolith, and chemical residues. Our data reveal a surprising beer recipe in which broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum), barley (Hordeum vulgare), Job's tears (Coix lacryma-jobi), and tubers were fermented together. The results indicate that people in China established advanced beer-brewing technology by using specialized tools and creating favorable fermentation conditions around 5,000 y ago. Our findings imply that early beer making may have motivated the initial translocation of barley from the Western Eurasia into the Central Plain of China before the crop became a part of agricultural subsistence in the region 3,000 y later.
Keywords: Yangshao period; alcohol; archaeological chemistry; phytolith analysis; starch analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Early evidence for beer drinking in a 9000-year-old platform mound in southern China.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 12;16(8):e0255833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255833. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34383818 Free PMC article.
-
The origins of specialized pottery and diverse alcohol fermentation techniques in Early Neolithic China.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jun 25;116(26):12767-12774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902668116. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31160461 Free PMC article.
-
Plant foods consumed at the Neolithic site of Qujialing (ca. 5800-4200 BP) in Jianghan Plain of the middle catchment of Yangtze River, China.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 18;13:1009452. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1009452. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36330240 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae- the main character in beer brewing.FEMS Yeast Res. 2008 Nov;8(7):1018-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00433.x. Epub 2008 Sep 15. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008. PMID: 18795959 Review.
-
Mold and mycotoxin problems encountered during malting and brewing.Int J Food Microbiol. 2007 Oct 20;119(1-2):89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.07.030. Epub 2007 Jul 31. Int J Food Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17727998 Review.
Cited by
-
Actional Mechanisms of Active Ingredients in Functional Food Adlay for Human Health.Molecules. 2022 Jul 27;27(15):4808. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154808. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Identification of HD-Zip Family Genes in Coix lacryma-jobi L. and Their Potential Roles in Response to Abiotic Stress.Plants (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;14(9):1318. doi: 10.3390/plants14091318. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364347 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Wine Fermentation: Unveiling Key Factors Shaping Quality, Flavor, and Technological Evolution.Foods. 2025 Jul 21;14(14):2544. doi: 10.3390/foods14142544. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decomposing the molecular complexity of brewing.NPJ Sci Food. 2020 Aug 20;4:11. doi: 10.1038/s41538-020-00070-3. eCollection 2020. NPJ Sci Food. 2020. PMID: 32885047 Free PMC article.
-
Wine or Beer? Comparison, Changes and Improvement of Polyphenolic Compounds during Technological Phases.Molecules. 2020 Oct 27;25(21):4960. doi: 10.3390/molecules25214960. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33120907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wen S, Yuan T. Yinxu Buci Yanjiu: Kexue Jishu Pian (A Study of Oracle Bones from Yinxu: Science and Technology) 1st Ed Sichuansheng Shehui Kexueyuan; Chengdu, China: 1983.
-
- Zhang D. Yinshang jiuwenhua chulun (A preliminary study of Shang alcohol culture) Zhongyuan Wenwu. 1994;3:19–24.
-
- Chen M. Yinxu Buci Zongshu (A Comprehensive Study of the Oracle Bone Inscriptions from Yinxu) Kexue; Beijing: 1956.
-
- Huang HT. Science and Civilisation in China. Vol 6: Biology and Biological Technology. Part V: Fermentations and Food Science. Cambridge Univ Press; Cambridge, UK: 2000.
-
- Li Y. Dui woguo niangjiu qiyuan de tantao (The origin of alcoholic beverages in China) Kaogu. 1962;1:41–44.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

