HER2 testing in gastric cancer: An update
- PMID: 27217694
- PMCID: PMC4870069
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4619
HER2 testing in gastric cancer: An update
Abstract
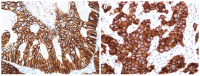
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression is increasingly recognized as a frequent molecular abnormality in gastric and gastroesophageal cancer. With the recent introduction of HER2 molecular targeted therapy for patients with advanced gastric cancer, determination of HER2 status is crucial in order to select patients who may benefit from this treatment. This paper provides an update on our knowledge of HER2 in gastric and gastroesophageal cancer, including the prognostic relevance of HER2, the key differences between HER2 protein expression interpretation in breast and gastric cancer, the detection methods and the immunohistochemistry scoring system.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing; Immunohistochemistry; Scoring system; Trastuzumab.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama T, Sudo C, Ogawara H, Toyoshima K, Yamamoto T. The product of the human c-erbB-2 gene: a 185-kilodalton glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity. Science. 1986;232:1644–1646. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Janjigian YY, Werner D, Pauligk C, Steinmetz K, Kelsen DP, Jäger E, Altmannsberger HM, Robinson E, Tafe LJ, Tang LH, et al. Prognosis of metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer by HER2 status: a European and USA International collaborative analysis. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:2656–2662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

